



ISSN 1004-132X
CN 42-1294/TH
CN 42-1294/TH




中国机械工程 ›› 2026, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (1): 223-232.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2026.01.023
• 工程前沿 • 上一篇
周彬1,2,3( ), 杨志峰1, 张峻宁1, 董元发1,2,3(
), 杨志峰1, 张峻宁1, 董元发1,2,3( ), 彭巍1,2,3
), 彭巍1,2,3
收稿日期:2024-12-20
出版日期:2026-01-25
发布日期:2026-02-05
通讯作者:
董元发
作者简介:周彬,男,1988年生,副教授。研究方向为人车共驾、车辆智能控制。发表论文40余篇。E-mail: zhoubin@ctgu.edu.cn基金资助:
ZHOU Bin1,2,3( ), YANG Zhifeng1, ZHANG Junning1, DONG Yuanfa1,2,3(
), YANG Zhifeng1, ZHANG Junning1, DONG Yuanfa1,2,3( ), PENG Wei1,2,3
), PENG Wei1,2,3
Received:2024-12-20
Online:2026-01-25
Published:2026-02-05
Contact:
DONG Yuanfa
摘要:
人-车共驾过程中,驾驶员的情绪变化会导致认知变化,进而改变车辆风险场,为此构建了一种考虑驾驶员认知-情绪状态的人因风险场模型。首先通过驾驶模拟器实验收集并分析车辆行驶数据和驾驶员生理信号;随后标定人因风险场中的驾驶员因子;最后通过六自由度驾驶模拟器采集实验数据并对人因风险场风险指标与多传统风险指标进行对比。人因风险场模型在边缘场景下能更有效和稳定评估不同情绪驾驶员的行车风险。
中图分类号:
周彬, 杨志峰, 张峻宁, 董元发, 彭巍. 边缘场景下计及驾驶员认知处理过程的驾驶风险场模型构建[J]. 中国机械工程, 2026, 37(1): 223-232.
ZHOU Bin, YANG Zhifeng, ZHANG Junning, DONG Yuanfa, PENG Wei. Construction of Driving Risk Field Model Considering Driver Cognitive Processing in Edge Scenes[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2026, 37(1): 223-232.
| 参数 | RMSE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 标定结果 | 0.0379 | 0.6741 | 0.5762 |
表1 风险场模型参数标定结果
Tab.1 Calibration results of risk field model parameters
| 参数 | RMSE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 标定结果 | 0.0379 | 0.6741 | 0.5762 |
| 指标 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 权重 | 0.0689 | 0.1659 | 0.1389 | 0.2436 | 0.1934 | 0.1893 |
表2 认知风险因子指标权重标定
Tab.2 Cognitive risk factor index weight calibration
| 指标 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 权重 | 0.0689 | 0.1659 | 0.1389 | 0.2436 | 0.1934 | 0.1893 |
| 合规车速驾驶 | 轻微超速驾驶 | 严重超速驾驶 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 情绪状态 | 频数 | 占比/% | 频数 | 占比/% | 频数 | 占比/% |
| 中性情绪 | 2893 | 96.40 | 60 | 2.00 | 48 | 1.60 |
| 正性情绪 | 2794 | 93.54 | 135 | 4.52 | 58 | 1.94 |
| 负性情绪 | 2428 | 82.00 | 448 | 14.93 | 92 | 3.07% |
表3 不同情绪状态下驾驶员超速行为频数和占比
Tab.3 The frequency and proportion of speeding behavior of drivers under different emotional states
| 合规车速驾驶 | 轻微超速驾驶 | 严重超速驾驶 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 情绪状态 | 频数 | 占比/% | 频数 | 占比/% | 频数 | 占比/% |
| 中性情绪 | 2893 | 96.40 | 60 | 2.00 | 48 | 1.60 |
| 正性情绪 | 2794 | 93.54 | 135 | 4.52 | 58 | 1.94 |
| 负性情绪 | 2428 | 82.00 | 448 | 14.93 | 92 | 3.07% |
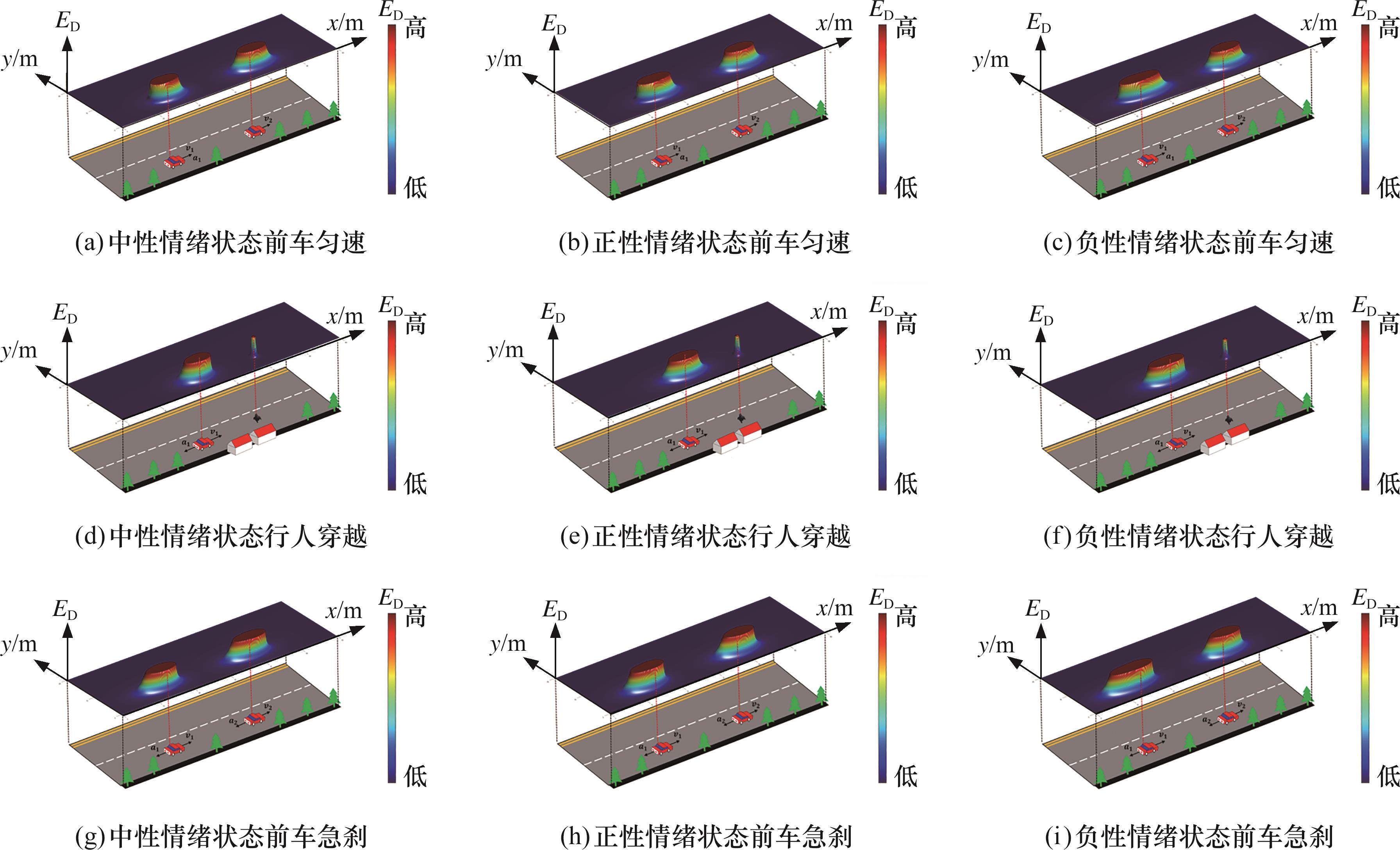
图12 不同情绪下HF-CRF三维示意图(ED为人因行为场场强)
Fig.12 Three-dimensional diagram of HF-CRF under different emotions (ED represents the field strength of the human behavior field)
| [1] | LIU H X, FENG Shuo. Curse of Rarity for Autonomous Vehicles[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15: 4808. |
| [2] | 杨超, 杨帆, 王伟达, 等. 基于时空风险的智能驾驶车辆避险决策规划[J]. 汽车工程, 2024, 46(6): 975-984. |
| YANG Chao, YANG Fan, WANG Weida, et al. Risk Avoidance Decision Planning for Intelligent Driving Vehicles Based on Spatiotemporal Risk[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2024, 46(6): 975-984. | |
| [3] | 任文浩, 赵晓华, 陈晨, 等. 网联碰撞预警信息系统对雾天高速公路驾驶行为的影响[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 53(2): 27-37. |
| REN Wenhao, ZHAO Xiaohua, CHEN Chen, et al. Impact of Connected Collision Warning Information System on Freeway Driving Behavior in Foggy Conditions[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2025, 53(2): 27-37. | |
| [4] | CHEN Di, LI Hao, JIN Zhicheng, et al. Risk-anticipatory Autonomous Driving Strategies Considering Vehicles’ Weights Based on Hierarchical Deep Reinforcement Learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2024, 25(12): 19605-19618. |
| [5] | 王安杰, 郑玲, 李以农, 等. 基于预测风险场的智能汽车主动避撞运动规划[J]. 汽车工程, 2021, 43(7): 1096-1104. |
| WANG Anjie, ZHENG Ling, LI Yinong, et al. Motion Planning for Active Collision Avoidance of Intelligent Vehicles Based on Predictive Risk Field[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2021, 43(7): 1096-1104. | |
| [6] | LI Linheng, GAN Jing, JI Xinkai, et al. Dynamic Driving Risk Potential Field Model under the Connected and Automated Vehicles Environment and Its Application in Car-following Modeling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(1): 122-141. |
| [7] | CHEN Zheng, WEN Huiying. Modeling a Car-following Model with Comprehensive Safety Field in Freeway Tunnels[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, Part A: Systems, 2022, 148(7): 04022040. |
| [8] | WANG Jianqiang, WU Jian, LI Yang. The Driving Safety Field Based on Driver–Vehicle–Road Interactions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2015, 16(4): 2203-2214. |
| [9] | SONG Dongjian, ZHAO Jian, ZHU Bing, et al. Subjective Driving Risk Prediction Based on Spatiotemporal Distribution Features of Human Driver’s Cognitive Risk[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2024, 25(11): 16687-16703. |
| [10] | 李文博, 刘羽婧, 张峻铖, 等. 驾驶员情绪-驾驶风险机理分析[J]. 机械工程学报, 2022, 58(22): 379-394. |
| LI Wenbo, LIU Yujing, ZHANG Juncheng, et al. Analysis of the Influence Mechanism of Driver’s Emotion on Driving Risk[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2022, 58(22): 379-394. | |
| [11] | NI Jie, XIE Wanying, LIU Yiping, et al. Driver Emotion Recognition Involving Multimodal Signals: Electrophysiological Response, Nasal-tip Temperature, and Vehicle Behavior[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, Part A: Systems, 2024, 150: 04023125. |
| [12] | SCHMIDT E, DECKE R, RASSHOFER R. Correlation between Subjective Driver State Measures and Psychophysiological and |
| Vehicular Data in Simulated Driving[C]∥2016 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV). Gotenburg, 2016: 1380-1385. | |
| [13] | LI Wenbo, LI Guofa, TAN Ruichen, et al. Review and Perspectives on Human Emotion for Connected Automated Vehicles[J]. Automotive Innovation, 2024, 7(1): 4-44. |
| [14] | PIZZO A, LAUSI G, BURRAI J, et al. Emotion Behind the Wheel: Unravelling the Impact of Emotional (Dys)Regulation on Young Driving Behaviour—a Systematic Review[J]. Sustainability, 2024, 16(8): 3384. |
| [15] | 李林恒, 甘婧, 曲栩, 等. 智能网联环境下基于安全势场理论的车辆跟驰模型[J]. 中国公路学报, 2019, 32(12): 76-87. |
| LI Linheng, GAN Jing, QU Xu, et al. Car-following Model Based on Safety Potential Field Theory under Connected and Automated Vehicle Environment[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2019, 32(12): 76-87. | |
| [16] | 戢晓峰, 王健, 徐迎豪, 等. 基于驾驶风格的山区公路穿村镇段行车风险场灵敏度分析[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2024, 24(6): 316-325. |
| JI Xiaofeng, WANG Jian, XU Yinghao, et al. Driving Style-based Sensitivity Analysis of Driving Risk Field in Mountain Highway Sections Passing through Villages and Towns[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2024, 24(6): 316-325. |
| [1] | 李健, 张凯, 王海斌, 王哲, 程经纬, 闫昶. 储罐底板轮式相控阵全聚焦成像及扫查系统设计[J]. 中国机械工程, 2025, 36(12): 3057-3063. |
| [2] | 封雨鑫, 刘坚, 邓宏贵, 余强, 王战, 叶浩泉. 激光高速高精加工非均匀有理B样条曲线插补方法[J]. 中国机械工程, 2025, 36(12): 3002-3009. |
| [3] | 耿宇航, 何雪明, 高宗. 基于NURBS啮合线的高效双螺杆转子自适应设计方法[J]. 中国机械工程, 2025, 36(12): 2837-2845. |
| [4] | 石宇昂, 张磊, 谢罗涛, 尹路晗. 船用汽轮机极端变工况流场扰动及稳定运行特性[J]. 中国机械工程, 2025, 36(10): 2258-2265. |
| [5] | 赵星宇, 赵铁石, 许博, 刘相权, 秦宇飞. 并联式混合驱动机构运动学和传递性能分析[J]. 中国机械工程, 2025, 36(08): 1728-1739. |
| [6] | 宋李俊, 刘松林, 辛玉, 马婧华, 谢正邱. 基于轴承退化状态评估和改进图注意力双向门控循环单元网络的轴承剩余寿命预测[J]. 中国机械工程, 2025, 36(07): 1562-1572. |
| [7] | 王永青, 艾靖超, 李特, 兰天, 刘海波. 虑及刚度特性的管内机器人高精度焊缝打磨方法[J]. 中国机械工程, 2025, 36(02): 351-358,368. |
| [8] | 刘怀举, 卢泽华, 朱才朝. 塑料齿轮传动高承载技术发展与应用[J]. 中国机械工程, 2025, 36(01): 2-17. |
| [9] | 徐腾, 邓春阳, 邱国强, 谢泽锋, 冉家琪, 龚峰. 纯钽薄壁构件高速级进拉深应变率效应及成形性研究[J]. 中国机械工程, 2024, 35(12): 2157-2168. |
| [10] | 张磊1, 2, 3, 孙学涛1, 2, 陈洁1, 2, 孙远波3, 郭佳佳1, 2, 郑杰1, 2. 汽车结构可靠性分析与优化设计研究进展[J]. 中国机械工程, 2024, 35(11): 1948-1962,1970. |
| [11] | 鄢威1, 3, 王欣怡2, 3, 张华3, 朱硕2, 3, 江志刚2, 3. 考虑切削能耗和表面质量的碳纤维增强树脂基复合材料加工工艺参数优化决策[J]. 中国机械工程, 2024, 35(10): 1834-1844. |
| [12] | 靳淇超1, 2, 包虎子1, 李良万3, 汪文虎3, 张锦淇1, 叶子银1, 郭磊1. DD5缓进磨削表面粗糙度和硬化率对疲劳性能影响研究[J]. 中国机械工程, 2024, 35(08): 1472-1479. |
| [13] | 倪涛1, 2, 张泮虹1, 2, 赵泽仁1, 2. 无力传感器的操纵手柄自适应变阻抗控制[J]. 中国机械工程, 2024, 35(06): 1034-1043,1051. |
| [14] | 刘竟飞1, 姜潮2, 倪冰雨2, 汪宗太3. 基于主动学习与贝叶斯深度神经网络的高维多输出不确定性传播方法[J]. 中国机械工程, 2024, 35(05): 792-801. |
| [15] | 刘满东, 彭珍瑞. 基于联合多重重建自编码器的桁架损伤识别[J]. 中国机械工程, 2024, 35(05): 840-850. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||