



ISSN 1004-132X
CN 42-1294/TH
CN 42-1294/TH




中国机械工程 ›› 2026, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (1): 92-104.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2026.01.011
郭万金1,2,3,4( ), 田玉祥1, 利乾辉1, 曹雏清2,5, 赵立军2,4, 徐明坤1, 刘孝恒1, 侯旭栋1
), 田玉祥1, 利乾辉1, 曹雏清2,5, 赵立军2,4, 徐明坤1, 刘孝恒1, 侯旭栋1
收稿日期:2024-11-06
出版日期:2026-01-25
发布日期:2026-02-05
通讯作者:
郭万金
作者简介:郭万金*(通信作者),男,1983年生,副教授、博士研究生导师。研究方向为工业机器人打磨主动柔顺控制。E-mail:guowanjin@chd.edu.cn。
基金资助:
GUO Wanjin1,2,3,4( ), TIAN Yuxiang1, LI Qianhui1, CAO Chuqing2,5, ZHAO Lijun2,4, XU Mingkun1, LIU Xiaoheng1, HOU Xudong1
), TIAN Yuxiang1, LI Qianhui1, CAO Chuqing2,5, ZHAO Lijun2,4, XU Mingkun1, LIU Xiaoheng1, HOU Xudong1
Received:2024-11-06
Online:2026-01-25
Published:2026-02-05
Contact:
GUO Wanjin
摘要:
为解决未知环境下环境参数的不确定导致的机器人恒力打磨自适应调节能力不足的问题,提出一种未知环境参数实时估计的机器人自适应变阻抗恒力控制方法。该方法将自适应滑模控制作为内环控制,将环境参数估计与自适应变阻抗控制作为外环控制。机器人平台实验结果表明,所提方法能较好地实现期望打磨力跟踪,对未知环境工况机器人打磨作业具有较高的自适应性。
中图分类号:
郭万金, 田玉祥, 利乾辉, 曹雏清, 赵立军, 徐明坤, 刘孝恒, 侯旭栋. 未知环境下机器人打磨自适应变阻抗恒力控制[J]. 中国机械工程, 2026, 37(1): 92-104.
GUO Wanjin, TIAN Yuxiang, LI Qianhui, CAO Chuqing, ZHAO Lijun, XU Mingkun, LIU Xiaoheng, HOU Xudong. Adaptive Variable Impedance Constant Force Control of Robotic Grinding under Unknown Environments[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2026, 37(1): 92-104.
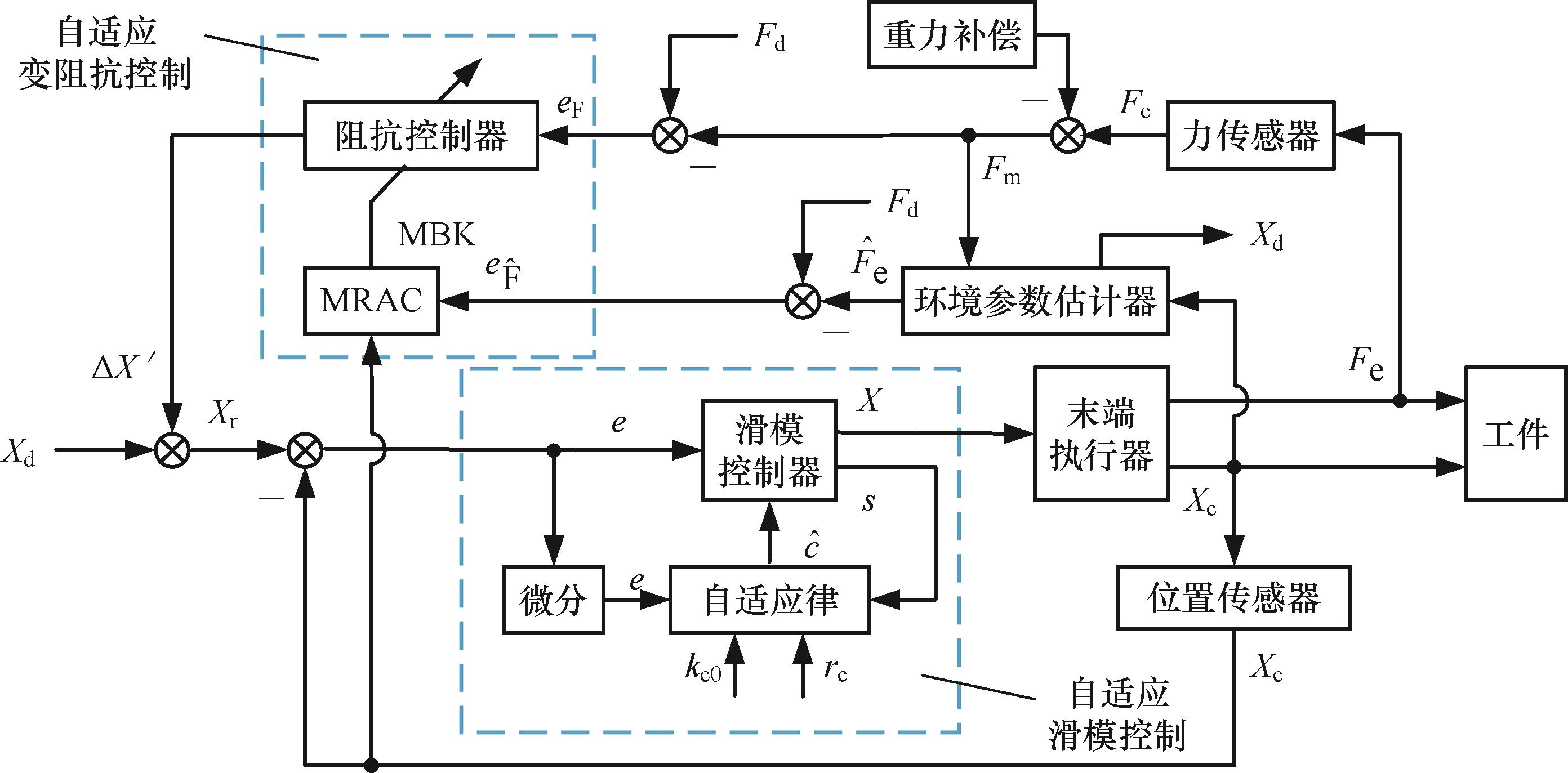
图3 未知环境参数实时估计的机器人自适应变阻抗恒力控制方法控制框图
Fig.3 Control block diagram of robotic adaptive variable impedance constant force control method with real-time estimation of unknown environmental parameters
期望打磨力20 N, 环境刚度150 MN/m | 期望打磨力30 N, 环境刚度200 MN/m | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 模糊阻抗控制 | 本文方法 | 模糊阻抗控制 | 本文方法 | |
| Fmax/N | 21.49 | 21.41 | 32.49 | 31.89 |
| Fmin/N | 18.19 | 18.54 | 27.26 | 28.17 |
| 19.77 | 19.97 | 29.80 | 29.87 | |
| EF /N | 0.23 | 0.03 | 0.20 | 0.13 |
| Fb/N | ±1.81 | ±1.46 | ±2.74 | ±1.89 |
| σF/% | 3.76 | 0 | 14.81 | 3.93 |
| tr/s | 0.40 | 1.21 | 0.22 | 0.13 |
| ts/s | 0.74 | 1.27 | 0.66 | 1.09 |
表1 不同恒定期望打磨力下机器人打磨力仿真实验结果
Tab.1 Simulation experiment results of robotic grinding force under different constant expected grinding forces
期望打磨力20 N, 环境刚度150 MN/m | 期望打磨力30 N, 环境刚度200 MN/m | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 模糊阻抗控制 | 本文方法 | 模糊阻抗控制 | 本文方法 | |
| Fmax/N | 21.49 | 21.41 | 32.49 | 31.89 |
| Fmin/N | 18.19 | 18.54 | 27.26 | 28.17 |
| 19.77 | 19.97 | 29.80 | 29.87 | |
| EF /N | 0.23 | 0.03 | 0.20 | 0.13 |
| Fb/N | ±1.81 | ±1.46 | ±2.74 | ±1.89 |
| σF/% | 3.76 | 0 | 14.81 | 3.93 |
| tr/s | 0.40 | 1.21 | 0.22 | 0.13 |
| ts/s | 0.74 | 1.27 | 0.66 | 1.09 |
| 打磨工况 | 控制方法 | EF /N | Fb/N | σF/% | tr/s | ts/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
斜坡信号动态期望打磨力 (下降斜坡) | 模糊阻抗控制 | 0.08 | 7.93 | 0.35 | 1.46 | |
| 本文方法 | 0.05 | 0 | 1.23 | 1.51 | ||
阶跃信号动态期望打磨力 (下降阶跃) | 模糊阻抗控制 | 0.18 | 7.93 | 0.35 | 1.45 | |
| 本文方法 | 0.13 | 0 | 1.24 | 1.50 | ||
| 余弦信号动态期望打磨力 | 模糊阻抗控制 | 0.16 | 7.93 | 0.35 | 1.47 | |
| 本文方法 | 0.15 | 0 | 1.25 | 1.54 |
表2 不同信号动态期望打磨力下机器人打磨力仿真实验结果
Tab.2 Simulation experiment results of robotic grinding force under different signal dynamic expected grinding force
| 打磨工况 | 控制方法 | EF /N | Fb/N | σF/% | tr/s | ts/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
斜坡信号动态期望打磨力 (下降斜坡) | 模糊阻抗控制 | 0.08 | 7.93 | 0.35 | 1.46 | |
| 本文方法 | 0.05 | 0 | 1.23 | 1.51 | ||
阶跃信号动态期望打磨力 (下降阶跃) | 模糊阻抗控制 | 0.18 | 7.93 | 0.35 | 1.45 | |
| 本文方法 | 0.13 | 0 | 1.24 | 1.50 | ||
| 余弦信号动态期望打磨力 | 模糊阻抗控制 | 0.16 | 7.93 | 0.35 | 1.47 | |
| 本文方法 | 0.15 | 0 | 1.25 | 1.54 |
| 打磨工况 | 控制方法 | Fmax/N | Fmin/N | EF /N | Fb/N | σF/% | tr/s | ts/s | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 期望打磨力20 N,铝板 | 模糊阻抗控制 | 22.17 | 17.01 | 19.37 | 0.63 | 11.0 | 0.08 | 0.98 | |
| 本文方法 | 22.13 | 18.23 | 20.02 | 0.02 | 0 | 0.56 | 0.66 | ||
| 期望打磨力30 N,铁板 | 模糊阻抗控制 | 36.52 | 22.20 | 29.79 | 0.21 | 30.63 | 0.32 | 0.82 | |
| 本文方法 | 32.43 | 26.58 | 30.01 | 0.01 | 4.67 | 0.14 | 0.26 | ||
| 期望打磨力40 N,铝板 | 模糊阻抗控制 | 45.23 | 38.43 | 41.66 | 1.66 | 20.22 | 0.10 | 1.78 | |
| 本文方法 | 44.10 | 36.64 | 40.17 | 0.17 | 10.75 | 0.11 | 1.52 | ||
| 期望打磨力40 N,铁板 | 模糊阻抗控制 | 48.99 | 33.84 | 41.33 | 1.33 | 41.25 | 0.06 | 1.97 | |
| 本文方法 | 45.36 | 33.13 | 38.96 | 1.04 | 18.50 | 0.10 | 1.91 |
表3 不同期望打磨力下机器人打磨力实验结果
Tab.4 Experimental results of robotic grinding force under different expected grinding forces
| 打磨工况 | 控制方法 | Fmax/N | Fmin/N | EF /N | Fb/N | σF/% | tr/s | ts/s | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 期望打磨力20 N,铝板 | 模糊阻抗控制 | 22.17 | 17.01 | 19.37 | 0.63 | 11.0 | 0.08 | 0.98 | |
| 本文方法 | 22.13 | 18.23 | 20.02 | 0.02 | 0 | 0.56 | 0.66 | ||
| 期望打磨力30 N,铁板 | 模糊阻抗控制 | 36.52 | 22.20 | 29.79 | 0.21 | 30.63 | 0.32 | 0.82 | |
| 本文方法 | 32.43 | 26.58 | 30.01 | 0.01 | 4.67 | 0.14 | 0.26 | ||
| 期望打磨力40 N,铝板 | 模糊阻抗控制 | 45.23 | 38.43 | 41.66 | 1.66 | 20.22 | 0.10 | 1.78 | |
| 本文方法 | 44.10 | 36.64 | 40.17 | 0.17 | 10.75 | 0.11 | 1.52 | ||
| 期望打磨力40 N,铁板 | 模糊阻抗控制 | 48.99 | 33.84 | 41.33 | 1.33 | 41.25 | 0.06 | 1.97 | |
| 本文方法 | 45.36 | 33.13 | 38.96 | 1.04 | 18.50 | 0.10 | 1.91 |
| [1] | 王田苗, 陶永. 我国工业机器人技术现状与产业化发展战略[J]. 机械工程学报, 2014, 50(9): 1-13. |
| WANG Tianmiao, TAO Yong. Research Status and Industrialization Development Strategy of Chinese Industrial Robot[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 50(9): 1-13. | |
| [2] | ZHU Dahu, FENG Xiaozhi, XU Xiaohu, et al. Robotic Grinding of Complex Components: a Step towards Efficient and Intelligent Machining—Challenges, Solutions, and Applications[J]. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2020, 65: 101908. |
| [3] | WANG Qilong, WANG Wei, ZHENG Lianyu, et al. Force Control-based Vibration Suppression in Robotic Grinding of Large Thin-wall Shells[J]. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2021, 67: 102031. |
| [4] | LI Dingwei, YANG Jixiang, ZHAO Huan, et al. Contact Force Plan and Control of Robotic Grinding towards Ensuring Contour Accuracy of Curved Surfaces[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2022, 227: 107449. |
| [5] | 葛吉民, 邓朝晖, 王水仙, 等. 基于点云的机器人焊缝自动化磨削系统与方法[J]. 中国机械工程, 2024, 35(7): 1253-1262. |
| GE Jimin, DENG Zhaohui, WANG Shuixian, et al. Automated Grinding System and Method for Robotic Weld Seams Based on Point Cloud[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2024, 35(7): 1253-1262. | |
| [6] | 葛吉民, 邓朝晖, 李尉, 等. 机器人磨抛力柔顺控制研究进展[J]. 中国机械工程, 2021, 32(18): 2217-2230. |
| GE Jimin, DENG Zhaohui, LI Wei, et al. Research Progresses of Robot Grinding and Polishing Force Compliance Controls[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 32(18): 2217-2230. | |
| [7] | ZENG Xi, ZHU Guangyi, GAO Zhuohan, et al. Surface Polishing by Industrial Robots: a Review[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2023, 125(9): 3981-4012. |
| [8] | KANA S, LAKSHMINARAYANAN S, MOHAN D M, et al. Impedance Controlled Human-robot Collaborative Tooling for Edge Chamfering and Polishing Applications[J]. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2021, 72: 102199. |
| [9] | 甘亚辉, 段晋军, 戴先中. 非结构环境下的机器人自适应变阻抗力跟踪控制方法[J]. 控制与决策, 2019, 34(10): 2134-2142. |
| GAN Yahui, DUAN Jinjun, DAI Xianzhong. Adaptive Variable Impedance Control for Robot Force Tracking in Unstructured Environment[J]. Control and Decision, 2019, 34(10): 2134-2142. | |
| [10] | WANG Guilian, DENG Yuxin, ZHOU Haibo, et al. PD-adaptive Variable Impedance Constant Force Control of Macro-mini Robot for Compliant Grinding and Polishing[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2023, 124(7): 2149-2170. |
| [11] | WAHBALLA H, DUAN Jinjun, DAI Zhendong. Constant Force Tracking Using Online Stiffness and Reverse Damping Force of Variable Impedance Controller for Robotic Polishing[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2022, 121(9): 5855-5872. |
| [12] | 陈满意, 朱自文, 朱义虎, 等. 曲面抛光机器人的模糊自适应阻抗控制[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2024, 30(6): 2090-2099. |
| CHEN Manyi, ZHU Ziwen, ZHU Yihu, et al. Fuzzy Adaptive Impedance Control of Surface Polishing Robot[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2024, 30(6): 2090-2099. | |
| [13] | 李路骋, 王振忠, 黄雪鹏. 基于模糊阻抗控制的机器人气囊抛光恒力控制系统研究[J]. 中国机械工程, 2025, 36(5): 1028-1034. |
| LI Lucheng, WANG Zhenzhong, HUANG Xuepeng. Research on Constant Force Control System of Robot Bonnet Polishing Based on Fuzzy Impedance Control[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2025, 36(5): 1028-1034. | |
| [14] | ZHONG Yichen, WANG Ting, PU Yanfeng, et al. An Adaptive Bilateral Impedance Control Based on Nonlinear Disturbance Observer for Different Flexible Targets Grasping[J]. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 2022, 103: 108388. |
| [15] | 严海堂, 钱牧云, 魏新园, 等. 机器人打磨系统力控补偿优化算法研究[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2024, 45(4): 272-281. |
| YAN Haitang, QIAN Muyun, WEI Xinyuan, et al. Research on Force Control Compensation Optimization Algorithm for Robotic Grinding System[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2024, 45(4): 272-281. | |
| [16] | TANG Zhiqiang, XIN Wenci, WANG Peiyi, et al. Learning-based Control for Soft Robot-environment Interaction with Force/Position Tracking Capability[J]. Soft Robotics, 2024, 11(5): 767-778. |
| [17] | 郭万金, 于苏扬, 赵伍端, 等. 机器人主动柔顺恒力打磨控制方法[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 44(1): 89-99. |
| GUO Wanjin, YU Suyang, ZHAO Wuduan, et al. Grinding Control Method of Robotic Active Compliance Constant-force[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2023, 44(1): 89-99. | |
| [18] | 郭万金, 于苏扬, 田玉祥, 等. 机器人打磨自适应变阻抗主动柔顺恒力控制[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2023, 55(12): 54-65. |
| GUO Wanjin, YU Suyang, TIAN Yuxiang, et al. Active Compliance Constant Force Control with Adaptive Variable Impedance for Robotic Grinding[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2023, 55(12): 54-65. | |
| [19] | 郭万金, 赵伍端, 利乾辉, 等. 基于集成概率模型的变阻抗机器人打磨力控制[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2023, 57(12): 2356-2366. |
| GUO Wanjin, ZHAO Wuduan, LI Qianhui, et al. Ensemble Probabilistic Model Based Variable Impedance for Robotic Grinding Force Control[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2023, 57(12): 2356-2366. | |
| [20] | 郭万金, 赵伍端, 于苏扬, 等. 无先验模型曲面的机器人打磨主动自适应在线轨迹预测方法[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2023, 57(8): 1655-1666. |
| GUO Wanjin, ZHAO Wuduan, YU Suyang, et al. Active Adaptive Online Trajectory Prediction for Robotic Grinding on Surface without Prior Model[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2023, 57(8): 1655-1666. | |
| [21] | ZHOU Bo, SUN Yuyao, LIU Wenbo, et al. Active Admittance Control with Iterative Learning for General-purpose Contact-rich Manipulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2025, 72(3): 2842-2851. |
| [22] | HAMEDANI M H, SADEGHIAN H, ZEKRI M, et al. Intelligent Impedance Control Using Wavelet Neural Network for Dynamic Contact Force Tracking in Unknown Varying Environments[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2021, 113: 104840. |
| [23] | 陈鹏飞, 李祥飞, 何显铭, 等. 基于薄壁零件刚度仿真到真实迁移的力控制研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2021, 57(17): 53-63. |
| CHEN Pengfei, LI Xiangfei, HE Xianming, et al. Research on Force Control Based on Sim2Real Transfer for Stiffness of Thin-walled Parts[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 57(17): 53-63. | |
| [24] | SHEN Yichao, LU Yan, ZHUANG Chungang. A Fuzzy-based Impedance Control for Force Tracking in Unknown Environment[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2022, 36(10): 5231-5242. |
| [25] | 邓建新, 袁邦颐, 黄秋林, 等. 基于工业机器人的复杂曲面磨抛关键技术综述[J]. 机械工程学报, 2024, 60(7): 1-21. |
| DENG Jianxin, YUAN Bangyi, HUANG Qiulin, et al. Review on the Key Technologies of Complex Surfaces Polishing Based on Robots[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2024, 60(7): 1-21. | |
| [26] | 陈满意, 朱义虎, 韩天勇, 等. 基于轨迹修正的曲面抛光机器人终端滑模导纳控制[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2024, 30(2): 593-600. |
| CHEN Manyi, ZHU Yihu, HAN Tianyong, et al. Terminal Sliding Mode Admittance Control of Surface Polishing Robot Based on Trajectory Correction[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2024, 30(2): 593-600. | |
| [27] | 吕播阳, 孟庆鑫, 肖怀, 等. 基于改进三元模型的波纹管型气动软体驱动器神经网络滑模控制[J]. 中国机械工程, 2024, 35(8): 1414-1425. |
| BoyangLYU, MENG Qingxin, XIAO Huai, et al. Neural Network Sliding Mode Control of Bellows-type Pneumatic Soft Actuators Based on Improved Ternary Model[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2024, 35(8): 1414-1425. | |
| [28] | 罗睿, 赵英杰, 金辉, 等. 基于力柔顺性的航天对接半物理仿真[J]. 机器人, 2024, 46(3): 330-338. |
| LUO Rui, ZHAO Yingjie, JIN Hui, et al. Semi-physical Simulation of Space Docking Based on Force Compliance[J]. Robot, 2024, 46(3): 330-338. | |
| [29] | 李振, 赵欢, 王辉, 等. 机器人磨抛加工接触稳态自适应力跟踪研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2022, 58(9): 200-209. |
| LI Zhen, ZHAO Huan, WANG Hui, et al. Research on Contact Steady-state Adaptive Force Tracking of Robot Grinding and Polishing[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2022, 58(9): 200-209. | |
| [30] | REI C, WANG Q, CHEN L, et al. Constant Force Grinding Controller for Robots Based on SAC Optimal Parameter Finding Algo |
| rithm[J]. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14: 14127. | |
| [31] | 龚辉, 方强, 李国强, 等. 基于模型参考自适应的AGV运动控制系统设计[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2022, 56(9): 1867-1875. |
| GONG Hui, FANG Qiang, LI Guoqiang, et al. Design of AGV Motion Control System Based on Model Reference Adaptive Method[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2022, 56(9): 1867-1875. | |
| [32] | FENG Hao, SONG Qianyu, YIN Chenbo, et al. Adaptive Impedance Control Method for Dynamic Contact Force Tracking of Robotic Excavators[J]. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management, 2022, 148(11):10.1061/(ASCE)CO. 1943-7862. 0002399. |
| [33] | 许家忠, 陈继元, 黄成. 筒类舱段主动柔顺对接策略[J]. 电机与控制学报, 2021, 25(9): 140-146. |
| XU Jiazhong, CHEN Jiyuan, HUANG Cheng. Active Compliant Docking Strategy for Barrel-type Cabins[J]. Electric Machines and Control, 2021, 25(9): 140-146. | |
| [34] | SERAJI H. Adaptive Admittance Control: an Approach to Explicit Force Control in Compliant Motion[C]∥Proceedings of the 1994 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. San Diego, 1994: 2705-2712. |
| [35] | 刘志恒, 赵立军, 李瑞峰, 等. 面向轮毂磨抛的手腕偏置机器人运动学快速求解方法[J]. 机械工程学报, 2022, 58(14): 126-136. |
| LIU Zhiheng, ZHAO Lijun, LI Ruifeng, et al. Fast Solution Method for the Kinematics of Wrist Offset Robot Oriented to Wheel Hub Grinding and Polishing[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2022, 58(14): 126-136. | |
| [36] | ZHU Renfeng, YANG Guilin, FANG Zaojun, et al. Hybrid Orientation/Force Control for Robotic Polishing with a 2R1T Force-controlled End-effector[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2022, 121(3): 2279-2290. |
| [1] | 李浩, 刘欣荣, 刘仪沁, 范狄庆. 基于改进自抗扰控制的高空风机叶片打磨机器人被动柔顺控制方法研究[J]. 中国机械工程, 2025, 36(08): 1832-1841. |
| [2] | 郭万金1, 2, 3, 4, 孙浩1, 利乾辉1, 田玉祥1, 曹雏清2, 赵立军2, 4. 轮毂毛刺机器人打磨刀路规划与工具姿态优化[J]. 中国机械工程, 2025, 36(06): 1222-1237. |
| [3] | 李路骋, 王振忠, 黄雪鹏. 基于模糊阻抗控制的机器人气囊抛光恒力控制系统研究[J]. 中国机械工程, 2025, 36(05): 1028-1034. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||