0 引言
数字孪生(digital twin)又称作数字双胞胎或数字镜像,是基于数字化形式在信息空间创建一个与物理实体等价的虚拟模型,通过数据与信息的融合交互实现虚拟模型模拟物理实体在现实情况下的行为,为物理实体的运作与管理提供更多的优化决策。
1994年,CHESHMEHDOOST等[1]首次提出了“虚拟数字”的概念,为之后数字孪生概念的提出做好了技术铺垫。2003年,GRIEVES[2]提出了“与物理产品等价的虚拟化表达”概念,这一概念在之后几年被称作“镜像空间模型”或“信息镜像模型”,模型主要应用于产品生命周期的管理。至此数字孪生的雏形已构建完成。
2011年, GRIEVES正式提出数字孪生体的概念[3],并明确数字孪生系统主要包含物理空间实体、虚拟空间的虚拟产品、物理空间和虚拟空间之间的数据信息交互接口3个方面。2012年,美国国家航空航天局将数字孪生应用于飞行器的维护和质量监测[4-6],同时给出了数字孪生的明确定义:数字孪生是指充分利用物理模型、传感器、运行历史等数据,集成多学科、多物理量、多尺度、多概率的仿真过程,在虚拟信息空间中对物理实体进行镜像映射,反映物理实体行为、状态或活动的全生命周期过程。但是由于通信技术和数据处理技术的局限,数字孪生没有得到迅速推行和使用。
此后,数字孪生技术逐渐运用到仿真、虚拟装配以及3D打印等领域当中[4]。2014年之后,伴随物联网技术、人工智能技术以及虚拟现实技术的迅速发展,数字孪生的应用逐步扩展到包括制造与服务的整个产品周期当中,并衍生出数字孪生车间、数字孪生驱动、数字孪生生产线等多种概念与模型。近3年,大数据处理技术和5G技术的日益成熟为数字孪生技术的应用提供了技术支持,同时随着工业4.0和智能制造等多个理念的提出和人们对产品质量要求的日益提高,数字孪生技术已成为一个研究热点。自2016 年以来,Gartner公司一直将数字孪生技术作为十大战略科技发展趋势之一[7]。根据Gartner近期的物联网实施调查结果,13%的实施物联网(IoT)项目的组织已经在使用数字孪生,62%的组织正在建立或计划这样做。
数字孪生技术虽然具有应用范围广泛的优点,可在设计、制造、服务多个阶段应用[8],但同时也存在研究时间短、涉及的关键技术多、在进行物理实体的模拟仿真时无法真正复制物理细节等不足,这些因素局限了数字孪生在实际生产中的应用。本文主要通过时间维度比较分析数字孪生研究的发展历程,同时将搜集到的论文基本信息进行比较,以了解数字孪生的研究现状;最后将两者进行综合性分析,追踪数字孪生研究热点及其未来发展趋势,为未来数字孪生的相关研究提供数据参考。
1 文献计量法分析过程
文献计量法的分析方法过程主要包括检索查询、数据集确定、数据分析以及数据的可视化处理4个步骤。在使用Web of Science(WoS)进行检索查询及数据集确定的过程中,查询包括数字孪生、数字链、虚拟数字化、虚拟数据以及数字孪生车间在内的关键词。文献检索的日期为2019-06-10,设定检索的出版年份为1990-1-1至2019-06-10,经人工排除无关的文献后,共获得与数字孪生相关的论文486篇。
将文献检索结果发送至科学评估参考工具InCites进行文献的数据分析与存储,再将数据导入Microsoft Excel 2016,通过Python 3.6调用Microsoft Excel 2016中整理完毕的数据,以气泡图和关联图的形式将分析结果可视化。
2 文献计量法分析结果
2.1 论文时间分布
如图1所示,数字孪生相关研究的论文自1994年开始发表,在前20年中仅发表论文81篇,占总发文量的16.6%。从2014年开始,信息技术、工业4.0和物联网相关概念与技术的提出促进了数字孪生研究的迅速发展,相关论文的发文量迅速增加,到2018年达到了论文发文量顶峰,单年发文量达179,占所有论文的36.8%。
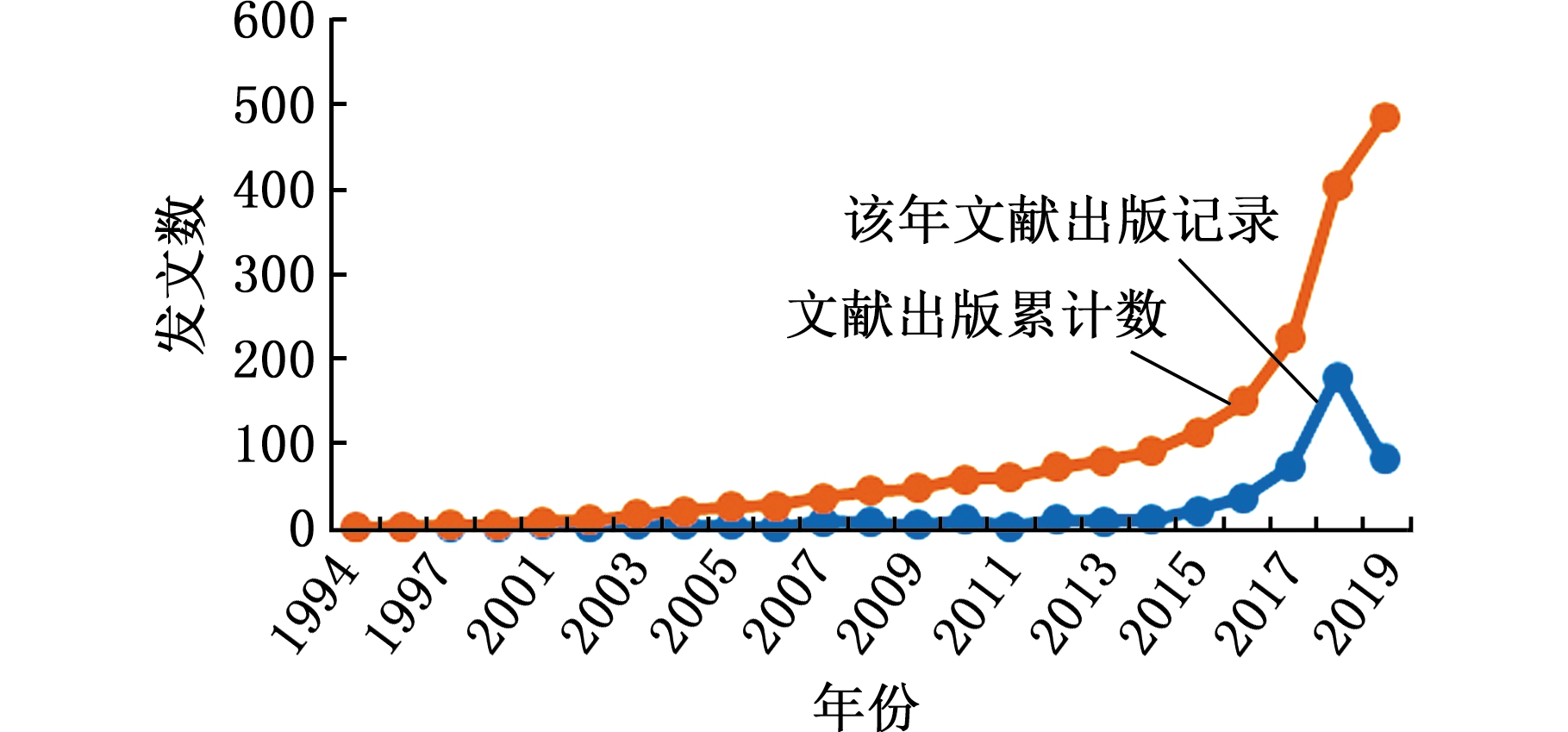
注:统计数据截止至2019-06-10。
图1 数字孪生领域论文发表趋势图
Fig.1 Trend chart of dissertation publication in digital twin field
2.2 相关论文国家/地区分布
通过文献分析,筛选出1994年以来发文量排名前20的国家/地区,见表1。美国是发文量最多的国家,共发表了90篇与数字孪生相关的论文。中国以80篇的发文量排名第二,德国则以65篇位居第三。排名第4至第6的国家/地区依次是英国、法国与意大利。从被引数及引文影响力角度分析可知,美国的数字孪生相关论文的被引频次(TC)高达455,是所有国家中最多的。德国(TC为202)、中国(TC为194)、法国(TC为111)的数字孪生相关论文也有较高的被引频次。虽然加拿大的发文量相对较少,但其学科引文影响力(CNCI)却是所有国家中最高的达到4.59。
在合作方面,结合表1与图2进行分析,在国家/地区相互关联图中,圆形坐标点半径越大表示发表论文数越多,而各坐标点之间连接线粗细则代表各国家/地区的合作紧密关系。由于表1中后10名国家/地区发文量较少,单篇合作论文对国际合作论文百分比影响较大,不能全面地反映一个国家在数字孪生研究方面的国际合作情况,故在进行论文的国际合作分析时,仅分析排名前10的国家与地区。分析可知,英国是所有国家中合作最为活跃的(国际合作论文百分比IC为63.33%),英国与美国、德国和西班牙的联系是最为紧密的,同时英国还和7成以上的前20国家/地区有过合作。美国、德国也是合作相对活跃的国家。除此之外,研究发现韩国的发文量虽排名第7,但韩国与其他国家的国际合作论文占比是排名前20国家中最低的(IC为0)。
2.3 数字孪生研究领域分布
研究领域反映了数字孪生相关课题的应用范围,表2展示了486篇数字孪生相关论文的研究领域。分析可知,数字孪生研究主要应用于工程、信息与控制等领域,是这些领域进行工程设计、模型仿真的一种有效技术手段。其中“工程、电气和电子”领域以99篇论文排名所有研究领域的第一。其次是“工程、制造”领域的70篇。发文量排名第3至第5名的领域分别是“计算机科学、信息系统”“计算机科学、理论与方法”和“自动化和控制系统”。数字孪生相关研究在“工程、制造”领域的发文量虽然排名第二,但是该领域在表2各项指标中均处于较高水平(CNCI为3.03,TC为273)。在该领域,TAO等[9]在2018年ICFDM会议发表的论文中提出了一种基于数字孪生驱动的产品设计、制造和服务的新方法,该文发表后近1年的被引次数达171,是该领域被引次数最多的一篇论文。而SCHLEICH等[10]与NEGRI 等[11]发表的有关数字孪生技术在工程制造领域应用的论文也有较高的被引频次。以上论文均表明,随着数字化手段的不断发展,数字孪生技术的应用已从产品的设计阶段逐渐延伸到产品的生产制造与服务阶段。
表1 数字孪生相关研究前20国家/地区发文量统计表
Tab.1 Statistics of top 20 countries/regions in digital twin related studies
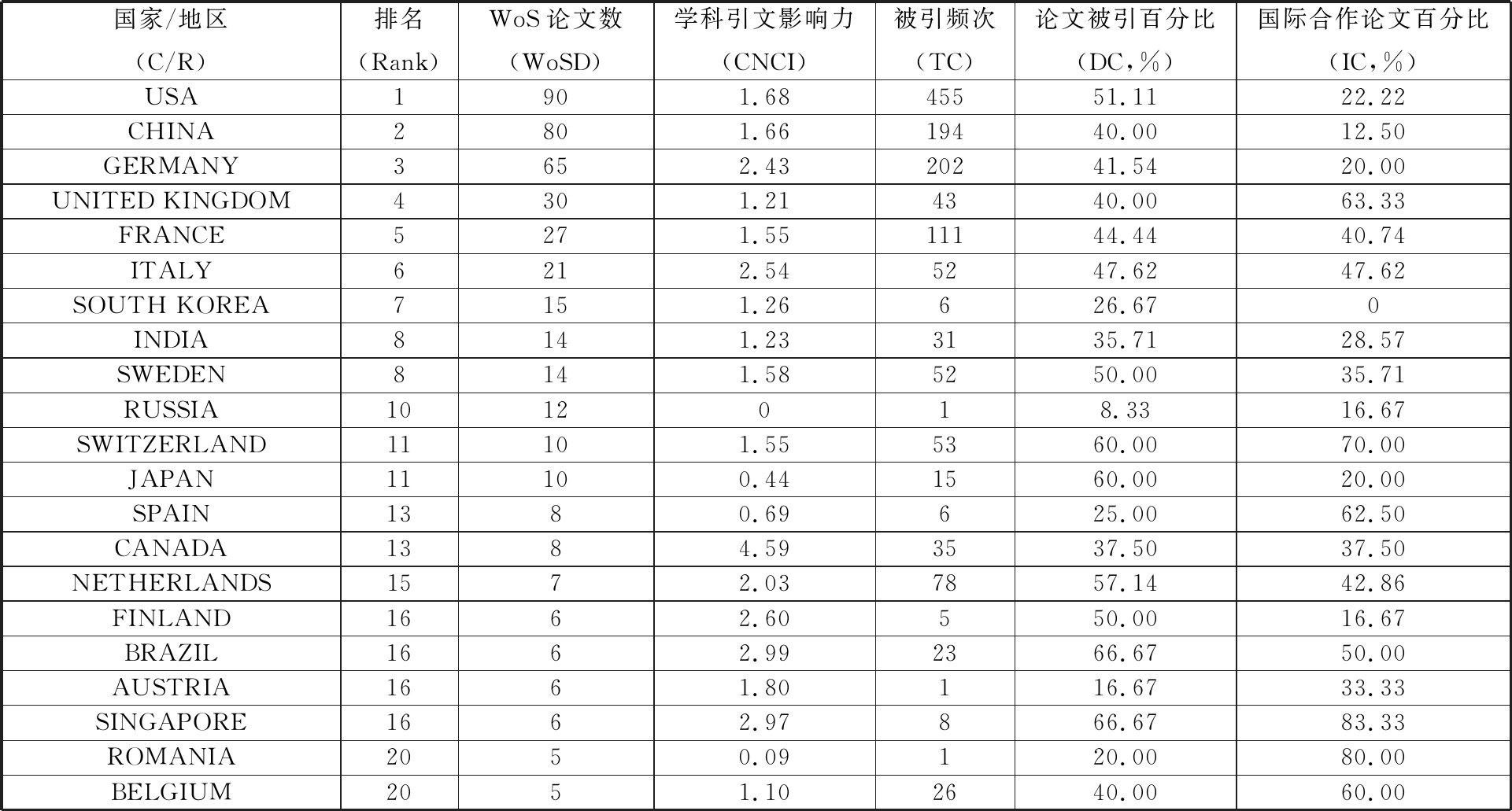
国家/地区(C/R)排名(Rank)WoS论文数(WoSD)学科引文影响力(CNCI)被引频次(TC)论文被引百分比(DC,%)国际合作论文百分比(IC,%)USA1901.6845551.1122.22CHINA2801.6619440.0012.50GERMANY3652.4320241.5420.00UNITED KINGDOM4301.214340.0063.33FRANCE5271.5511144.4440.74ITALY6212.545247.6247.62SOUTH KOREA7151.26626.670INDIA8141.233135.7128.57SWEDEN8141.585250.0035.71RUSSIA1012018.3316.67SWITZERLAND11101.555360.0070.00JAPAN11100.441560.0020.00SPAIN1380.69625.0062.50CANADA1384.593537.5037.50NETHERLANDS1572.037857.1442.86FINLAND1662.60550.0016.67BRAZIL1662.992366.6750.00AUSTRIA1661.80116.6733.33SINGAPORE1662.97866.6783.33ROMANIA2050.09120.0080.00BELGIUM2051.102640.0060.00
注:统计数据截至2019-06-10。
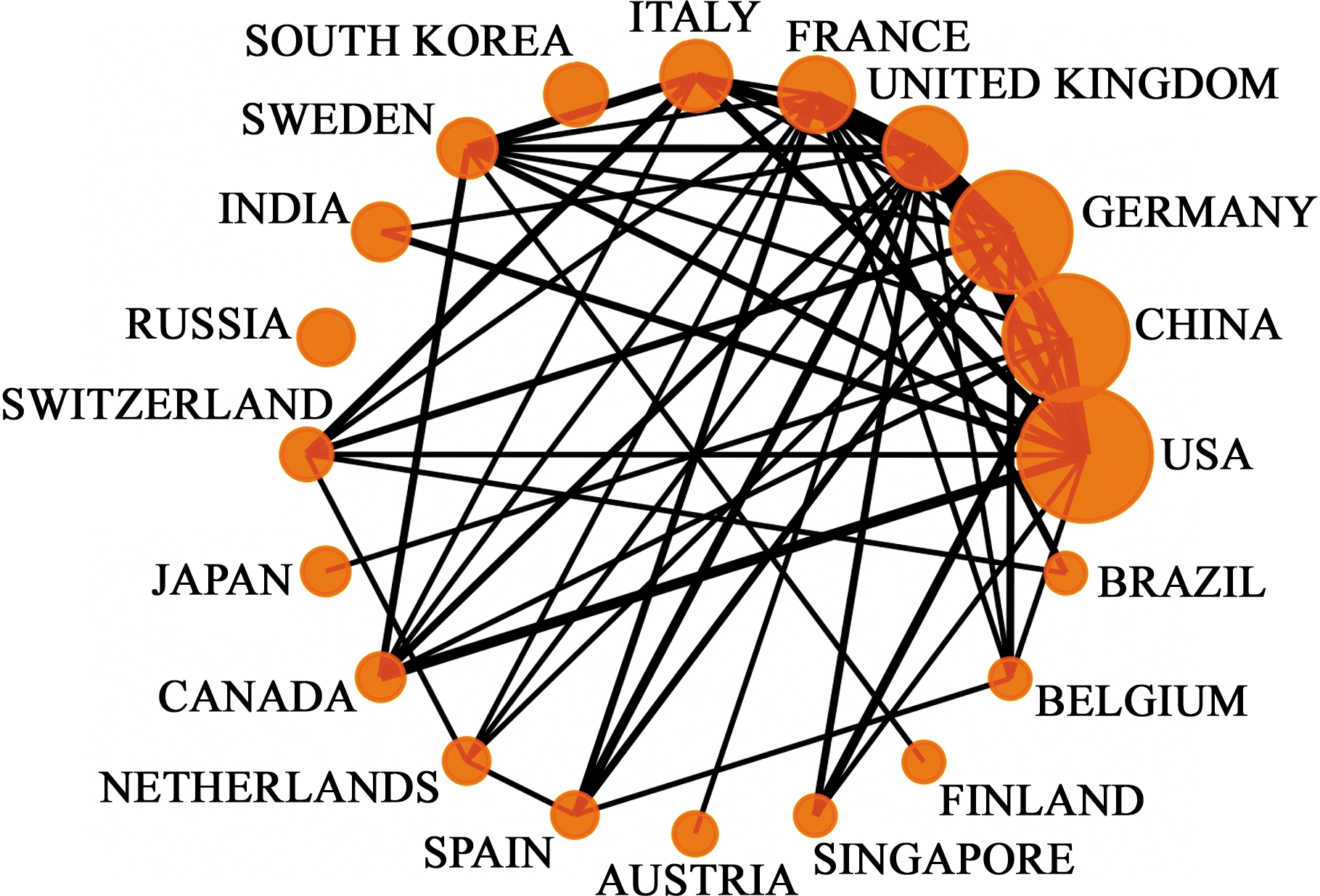
图2 数字孪生相关研究国家/地区关联图
Fig.2 Countries/regions Association Map of Digital Twin Related Studies
研究领域的气泡图见图3,气泡的半径大小表示在该年内的论文发文量。通过气泡图的纵向比较可以了解不同领域在同一时间的研究热门程度,通过横向比较可以了解某一研究领域的发展趋势与研究的现状。从图3中可以发现,数字孪生的研究在1994年最早应用于“工程、电气和电子”领域,在此之后的22年里,数字孪生在各研究领域的发展均比较缓慢。2016年是数字孪生在各研究领域迅速发展的时间节点。自2016年起,数字孪生在各热门领域每年的发文量以50%的增幅开始增长。
从研究热门程度分析,“工程、电气和电子”领域的研究热度一直保持在较高的水平上,该领域在2017至2019年间发文量分别为20篇、41篇、14篇,是数字孪生研究的一个重要领域。“工程、制造”领域是一个较新的研究领域,该领域有关数字孪生论文最早出现在2011年,但是在近3年得到了迅速的发展,2017至今,发文量已经达到76篇,该时间段发文量已成为所有研究领域的第一位。同时数字孪生在“计算机科学、理论与方法”等多个领域在近3年同样也有显著的发展。
2.4 数字孪生发布期刊分布分析
了解出版数字孪生研究的期刊有助于学者进行期刊筛选和论文的投递。因会议性期刊具有其特定的主题,会对本文的研究产生干扰,故仅对198篇非会议型论文进行文献计量法分析。 结果表明,数字孪生研究刚刚兴起,仅有128家期刊对数字孪生研究的论文进行了出版,并且论文的发布较为分散。表3显示了发文量排前20的期刊,IEEE Access[12-21]期刊以9篇的发文量成为发表数字孪生相关研究最多的期刊(TC为82,DC为44.44%),同时其被引频次也达到所有期刊中最多的94。International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing(TC为1;IF为1.83)发表论文8篇[22-29],排名第二,该期刊发表的论文均在2018—2019年间发布,且有一部分还未正式发布,因此总被引频次仅为1。Journal of Manufacturing Systems[30-35]、CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology[10,36-40]、International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology[9,41-45]三种期刊均以6篇的发文量排名并列第三。就期刊影响因子而言,IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics以6.36的系数成为发文量排名前20期刊中的第一。
表2 数字孪生相关研究领域发文统计表
Tab.2 Statistical tables of publications in dgitaltwin related research areas
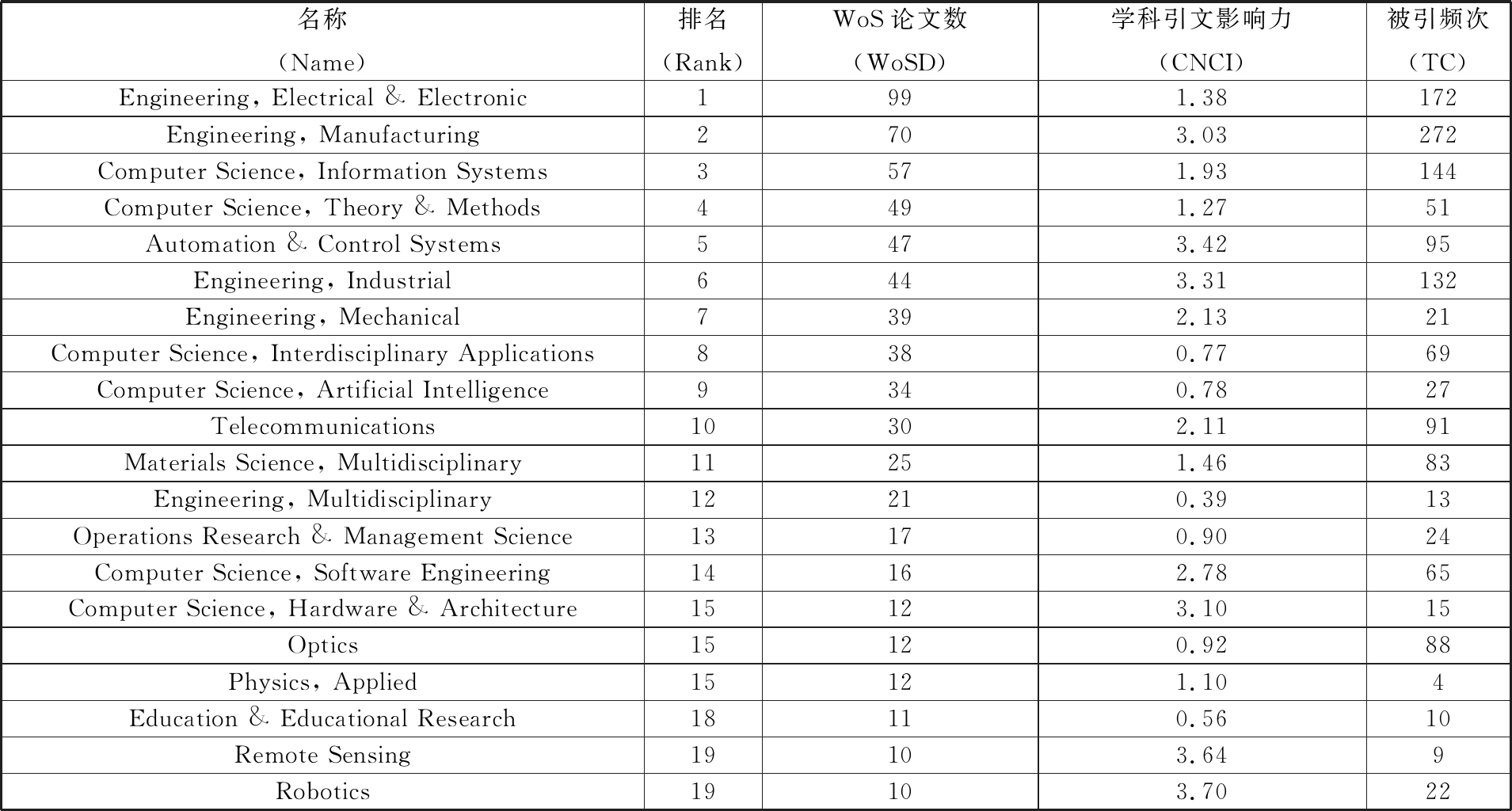
名称(Name)排名(Rank)WoS论文数(WoSD)学科引文影响力(CNCI)被引频次(TC)Engineering, Electrical & Electronic1991.38172Engineering, Manufacturing2703.03272Computer Science, Information Systems3571.93144Computer Science, Theory & Methods4491.2751Automation & Control Systems5473.4295Engineering, Industrial6443.31132Engineering, Mechanical7392.1321Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications8380.7769Computer Science, Artificial Intelligence9340.7827Telecommunications10302.1191Materials Science, Multidisciplinary11251.4683Engineering, Multidisciplinary12210.3913Operations Research & Management Science13170.9024Computer Science, Software Engineering14162.7865Computer Science, Hardware & Architecture15123.1015Optics15120.9288Physics, Applied15121.104Education & Educational Research18110.5610Remote Sensing19103.649Robotics19103.7022
注:统计数据截至2019-06-10。
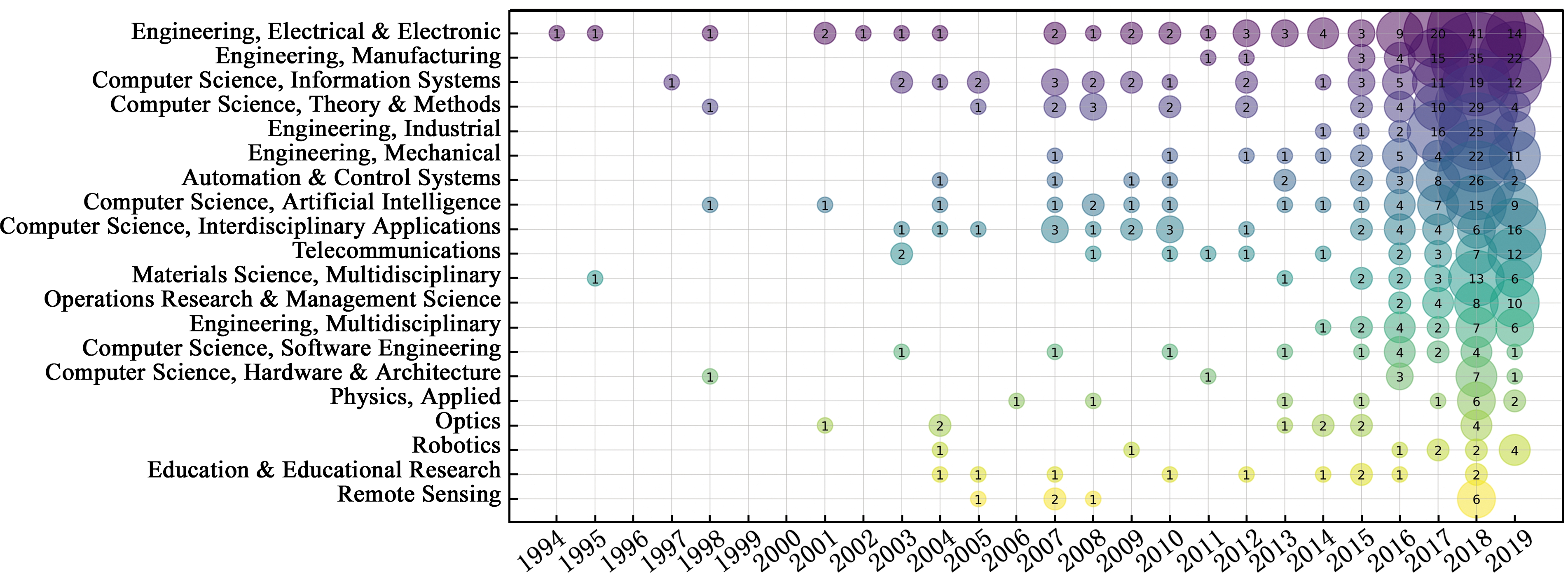
图3 数字孪生相关研究领域气泡图
Fig.3 Bubble diagrams in digital twin related research fields
为了更好地了解发文量前20的期刊发文趋势,对这些期刊进行分析,如图4所示。从2006年开始,逐步有相关的论文发表在表3所示的期刊上。2017年至今,发文量开始迅速上升,这也说明数字孪生研究进入了快速发展阶段。经过对各期刊的详细研究得知,在IEEE Access、International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing与Journal of Manufacturing Systems期刊上发表的论文主要以计算机通信领域、工程领域、信息领域与系统领域的论文居多,而Journal of Manufacturing Systems期刊发表的论文主要与运筹学领域相关,International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology期刊则主要涉及自动化控制系统相关领域的研究。对上述期刊研究领域进行分析可知,发表数字孪生相关论文的期刊涉及但不局限于工程、计算机通信、运筹学、制造领域。
表3 数字孪生相关研究期刊发文统计表
Tab.3 Statistical table of publications of digital twin related research periodicals
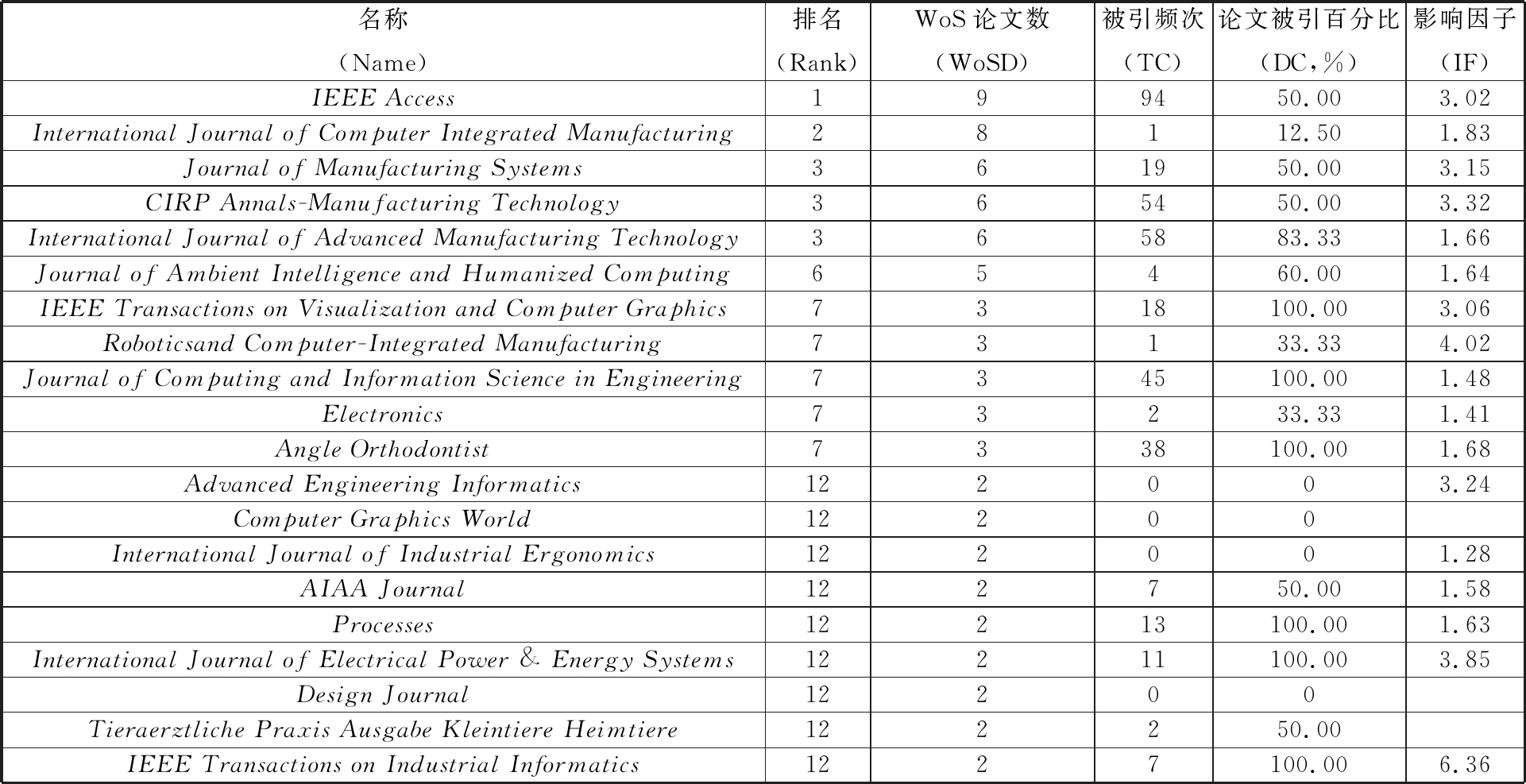
名称(Name)排名(Rank)WoS论文数(WoSD)被引频次(TC)论文被引百分比(DC,%)影响因子(IF)IEEE Access199450.003.02International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing28112.501.83Journal of Manufacturing Systems361950.003.15CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology365450.003.32International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology365883.331.66Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing65460.001.64IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics7318100.003.06Roboticsand Computer-Integrated Manufacturing73133.334.02Journal of Computing and Information Science in Engineering7345100.001.48Electronics73233.331.41Angle Orthodontist7338100.001.68Advanced Engineering Informatics122003.24Computer Graphics World12200International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics122001.28AIAA Journal122750.001.58Processes12213100.001.63International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems12211100.003.85Design Journal12200Tieraerztliche Praxis Ausgabe Kleintiere Heimtiere122250.00IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics1227100.006.36
注:统计数据截止至2019-06-10。
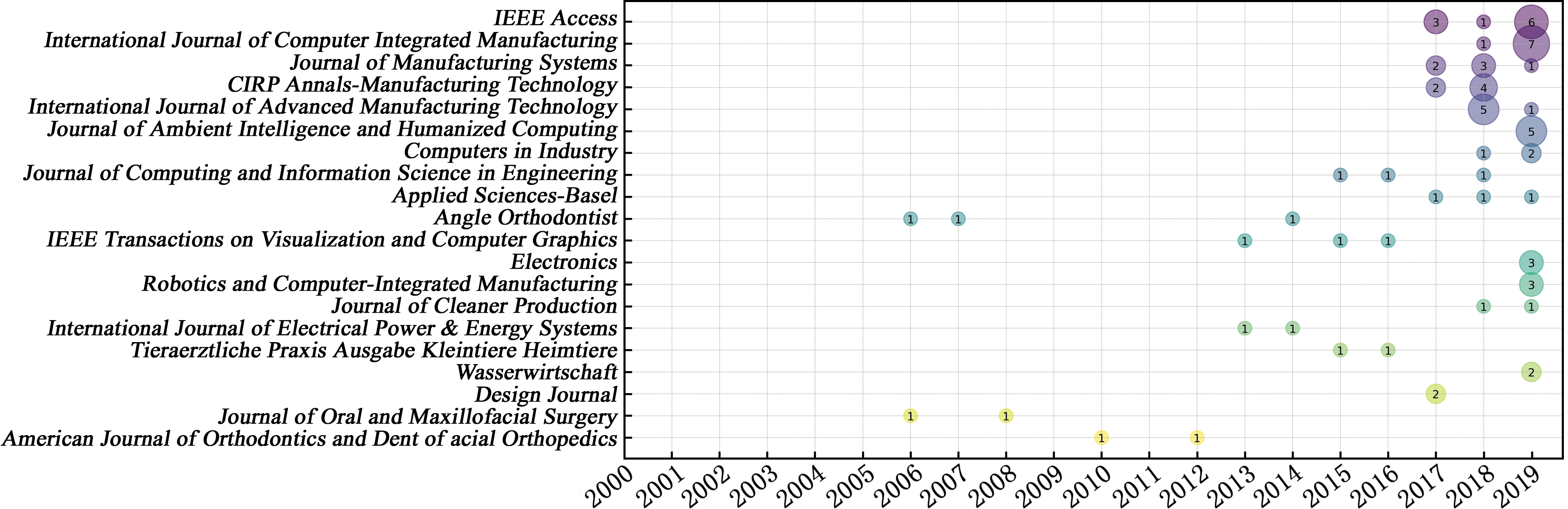
图4 数字孪生相关研究发布期刊分布气泡图
Fig.4 Bubble diagram of journal distribution of digital twin relevant research publications
2.5 关键词分析
为了揭示数字孪生相关领域的主要焦点问题和研究趋势,对486篇论文进行关键词分析,分析表明数字孪生的应用非常广泛,使用频率前20的关键词气泡图如图5所示。“数字孪生”关键词共被使用了117次,排名第一。在获取的数据当中,“数字孪生”关键词首次出现在2010年,且在2018年该关键词的出现频数达到了顶峰,排名第二的“工业4.0”关键词被使用25次。数字孪生技术于2016年由SCHROEDER等[46]首次应用于工业4.0领域,他们以数字孪生为技术基础,进行制造服务系统模型的建立与模拟。“仿真”关键词以20次使用频数排名第三,ROSEN等[47]认为数字孪生技术在模型建立与仿真过程当中可以对数据进行有效的诊断和优化,将会成为未来制造业的重要驱动力之一。而“智能制造”“数据链”“物联网”这几个与人工智能、虚拟现实相关的关键词在近3年频繁出现,并迅速成为数字孪生研究的热门研究问题,以17次、15次、13次的使用频数分列气泡图的第4、第6、第7名。TAO等[13]在2017年使用数字孪生技术将物理世界与虚拟世界结合起来,提出了一种基于数字孪生的数字孪生车间模型。该研究囊括了数字孪生车间、大数据、工业4.0等应用领域,为数字孪生在智能制造领域的应用拓展提供了一种新思路。由于在近3年通信技术的迅速发展与制造业的改革创新,排名前20的相关关键词在论文中的使用频数也迅速增加。
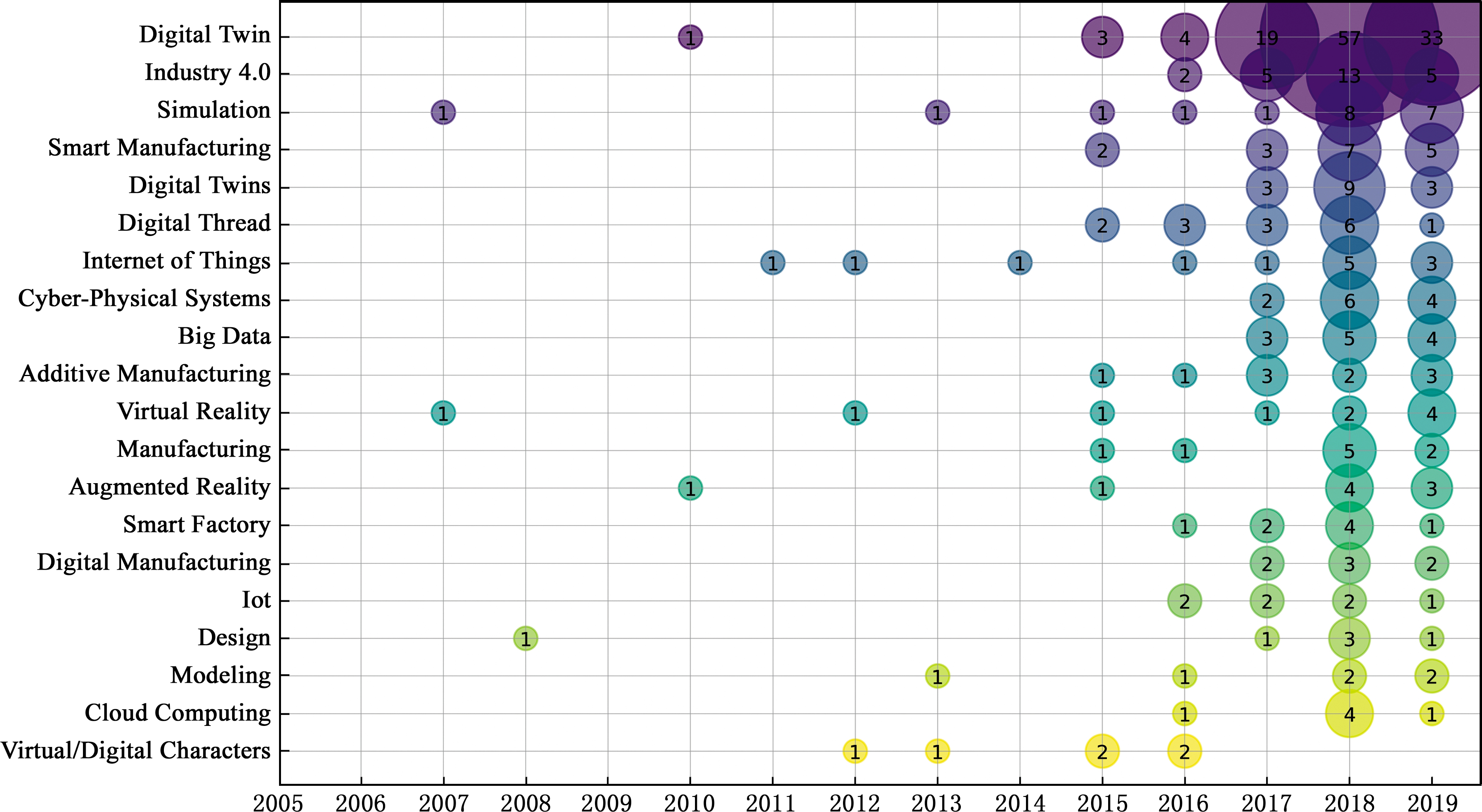
图5 数字孪生相关研究关键词气泡图
Fig.5 Bubble diagram of digital twin related research key words
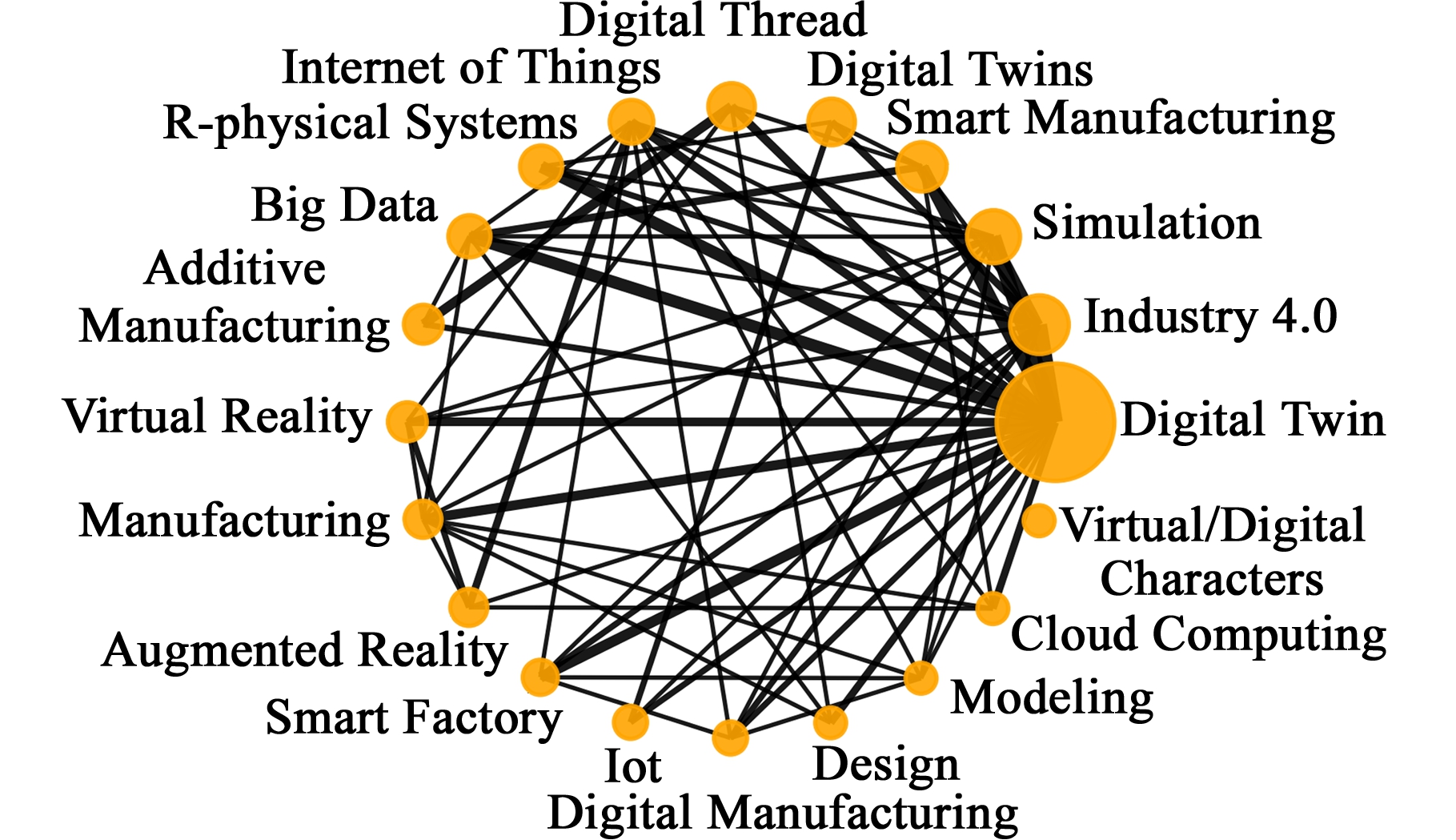
图6 数字孪生相关研究关键词关联图
Fig.6 Digital twin related research key word association diagram
图6展示了使用数字孪生研究频数前20关键词之间的相互关系,数字孪生技术是一门基于多学科的应用技术,其应用的领域较为广泛,并主要集中在模拟仿真、产品的制造、虚拟现实等领域,因此“数字孪生”关键词与“智能制造”“大数据”“信息物理系统”等多个关键词之间的关系最为紧密,而其余关键词之间并没有孤岛现象的产生。QI等[14]于2018年发表了一篇有关数字孪生技术在产品设计、生产计划、制造和预测维护中应用的综述性论文,阐述了大数据与数字孪生之间的异同,并认为数据孪生与大数据将会是智能制造未来可以迅速发展的关键技术之一。而WEYER等[48]提出了一种基于CPS的汽车加工工厂建模与仿真的框架,该模型主要运用物联网与数字孪生技术把物理世界与信息世界联系起来,以应对瞬息万变的市场需求。伴随着此类设想的不断提出,数字孪生技术将在产品生命周期的每个阶段都扮演一种不可或缺的角色。
由以上关键词的分析可知,随着近年智能制造与工业4.0的提出,数字孪生得到了迅速的发展,数字孪生与大数据、物联网等信息化技术相互结合,通过数字孪生工厂、信息物联等多种手段,为工程项目的建模、仿真与数据分析提供了一种更为高效的解决方法。
2.6 研究作者分布
由于数字孪生的研究起步较晚,目前相关作者发表的论文数量与被引频次普遍较少。从发文量角度分析,在数字孪生领域产出最多的学者是来自德国亚琛工业大学的ROSSMANN [25,49-50],共产出论文12篇(2.47%)。其次是来自中国北京航空航天大学的TAO [9,13,14,37,42,51-52],共发表论文9篇(1.85%),同时该作者发表的论文被引频次是所有作者中最多的(TC为389),TAO主要将数字孪生应用于工程、计算机科学和自动控制领域。来自瑞典查尔姆斯理工大学的SODERBERG[36]和来自美国国家标准技术研究所与HEDBERG[53-54]均以5篇的论文数排名第三。而表4中其他作者论文数基本集中在3~4之间。
从作者之间的关联程度分析,获得图7所示结果。ROSSMANN和ATORF、SCHLUSE之间有着较为紧密的联系[49,50,55],他们主要将数字孪生引入系统的建模仿真过程中,利用数字孪生减少仿真过程中的复杂程度。TAO与发文量排名并列第5的ZHANG来自同一个研究机构,他们对数字孪生车间方向的研究有着独到的见解,他们将数字孪生技术应用于数据管理和虚拟现实数据之间的转换,通过物理世界和虚拟世界的相互连接,提高管理和制造效率,降低成本[9,13,51,37]。而在所有的作者中,SODERBERG等[36,39]主要将数字孪生应用于模拟加工策略以保证最终产品的良好几何质量,该作者与LINDKVIST、MATHIEU、CARLSON等学者均有合作关系,是最为活跃的作者之一。
表4 数字孪生相关研究作者发文统计表
Tab.4 Statistics of authors' publications in digital twin related studies

作者(Author)排名(Rank)论文数(WoSD)被引频次(TC)所属机构(Research institutions)ROSSMANN J11242RWTH Aachen UniversityTAO Fei29389Beihang UniversitySODERBERG R3568Chalmers University of TechnologyHEDBERG T3572National Institute of Standards & Technology(NIST)-USAZHANG MENG54270Beihang UniversityANWER N54124Universite Paris Sud-Paris 11Ecole Normale Superieure Paris-SaclayUniversite Paris SaclayMATHIEU L54120Universite Paris Sud-Paris 11Ecole Normale Superieure Paris-SaclayUniversite Paris SaclayDEBROY T5492Penn State UniversityHELU M5444National Institute of Standards & Technology(NIST)-USALINDKVIST L5421Chalmers University of TechnologyQI Qinglin113287Beihang UniversityXU Xun11362University of AucklandLIU Qiang11354Guangdong University of TechnologyBARNARD F A11346National Institute of Standards & Technology(NIST)-USASCHLUSE M11338RWTH Aachen UniversityATORF L11327RWTH Aachen UniversityCARLSON J S11321Fraunhofer-Chalmers Research Centre for Industrial MathematicsMUKHERJEE T11319Penn State UniversityBONNARD R11313 LENG Jiewu11311Guangdong University of Technology
注:统计数据截至2019—11—10。
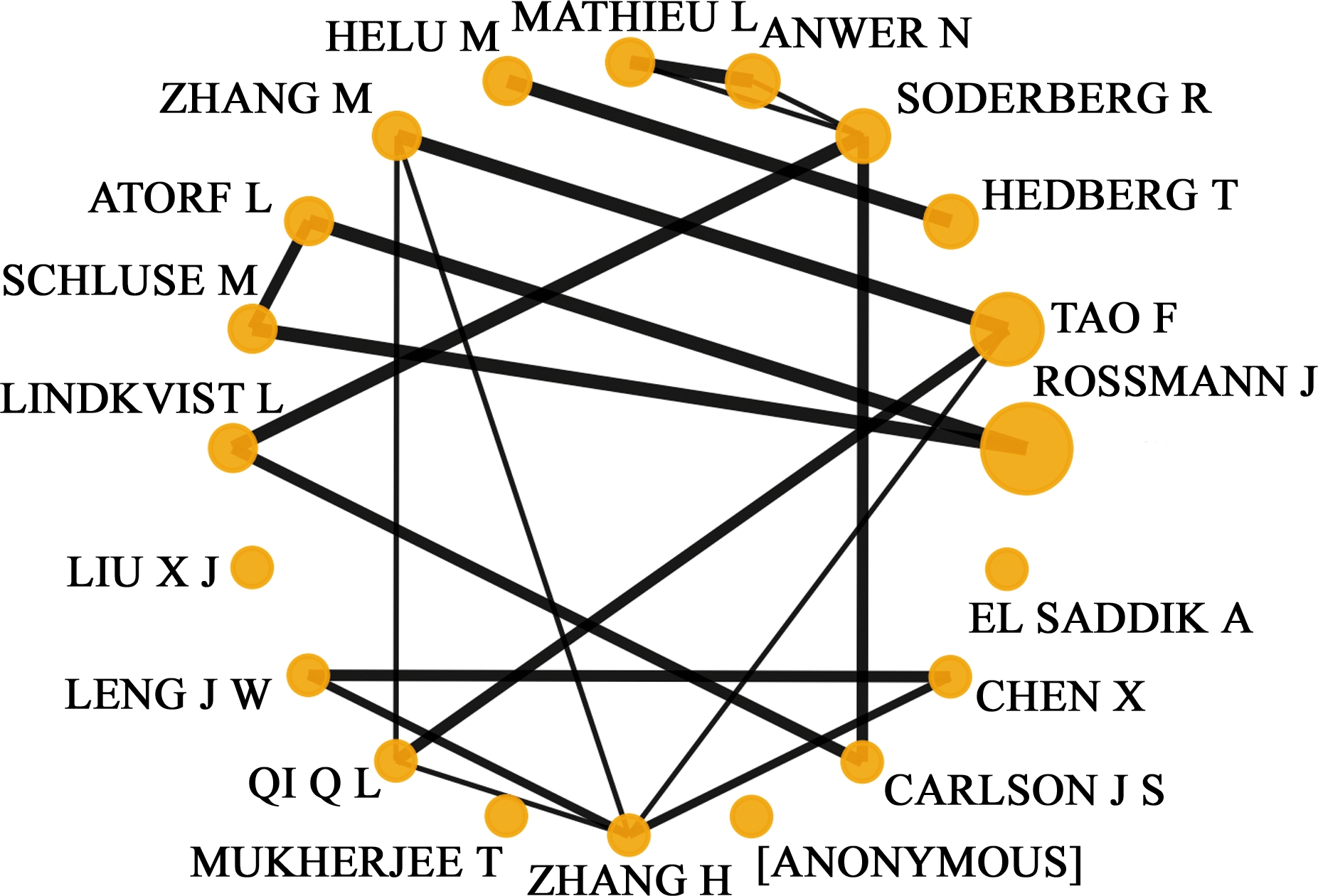
图7 数字孪生相关研究作者关联图
Fig.7 Authors’ association diagram of digital twin related studies
2.7 数字孪生高被引论文分析
一篇论文的被引频次可以反映出其科学价值和研究意义,表5列出了1994—2019年被引频次前20与数字孪生相关的论文。
被引频次最多的是TAO等[9]在2018年发表于International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 期刊上的名为Digital Twin-driven Product Design, Manufacturing and Service with Big Data的论文,该论文在一年中被引171次。该论文认为在智能制造背景下,以大数据为基础的数字孪生技术可以应用于产品的整个生产周期,在产品的设计阶段利用数字孪生可以提高设计的准确性,并验证产品在真实环境中的性能。在产品的生产制造阶段,数字孪生可以减少产品导入的时间,同时提高产品质量、降低产品的生产成本;而在产品的服务阶段,数字孪生可以通过数据的分析对产品进行优化,从而避免产品的故障发生概率,改善对客户的服务质量。
被引频次排名第二的是ROSEN等[47]于2013年在IFAC Papersonline期刊上发表的名为About the Importance of Autonomy and Digital Twins for the Future of Manufacturing的论文,该论文共被引用140次。这是一篇综述性论文,主要探讨未来驱动制造业4个重要的方面:模块化、连接、自主、数字孪生技术。该论文认为,数字孪生技术不仅可以将系统中各个模块化的数据进行连接,还是未来建模仿真的核心技术之一,将会推动仿真研究到达一个新的研究高度。该论文还认为,数字孪生技术是生产自治系统的一项核心技术,通过数字孪生可以使自主学习系统和设备获得先验性知识,为后续的自主学习提供数据支持,从而获得满意的结果。引用频次排名第三的是SCHLECH等[10]于2017年发表的名为Shaping the Digital Twin for Design and Production Engineering的论文,该论文主要设计了一种应用于生产制造过程当中的数字孪生模型,详细探讨了该模型的具体特性与应用。除此之外,UHLEMANN等则对数字孪生在工业4.0背景下的网络物理生产系统进行了详细的研究。其他高被引论文详见表5。由表5可知,数字孪生高被引的论文主要集中在智能制造领域,且逐渐被许多学者认为是未来实现智能制造的核心驱动力之一。
表5 数字孪生高被引论文统计表
Tab.5 Statistical table of highly cited papers with digital twins
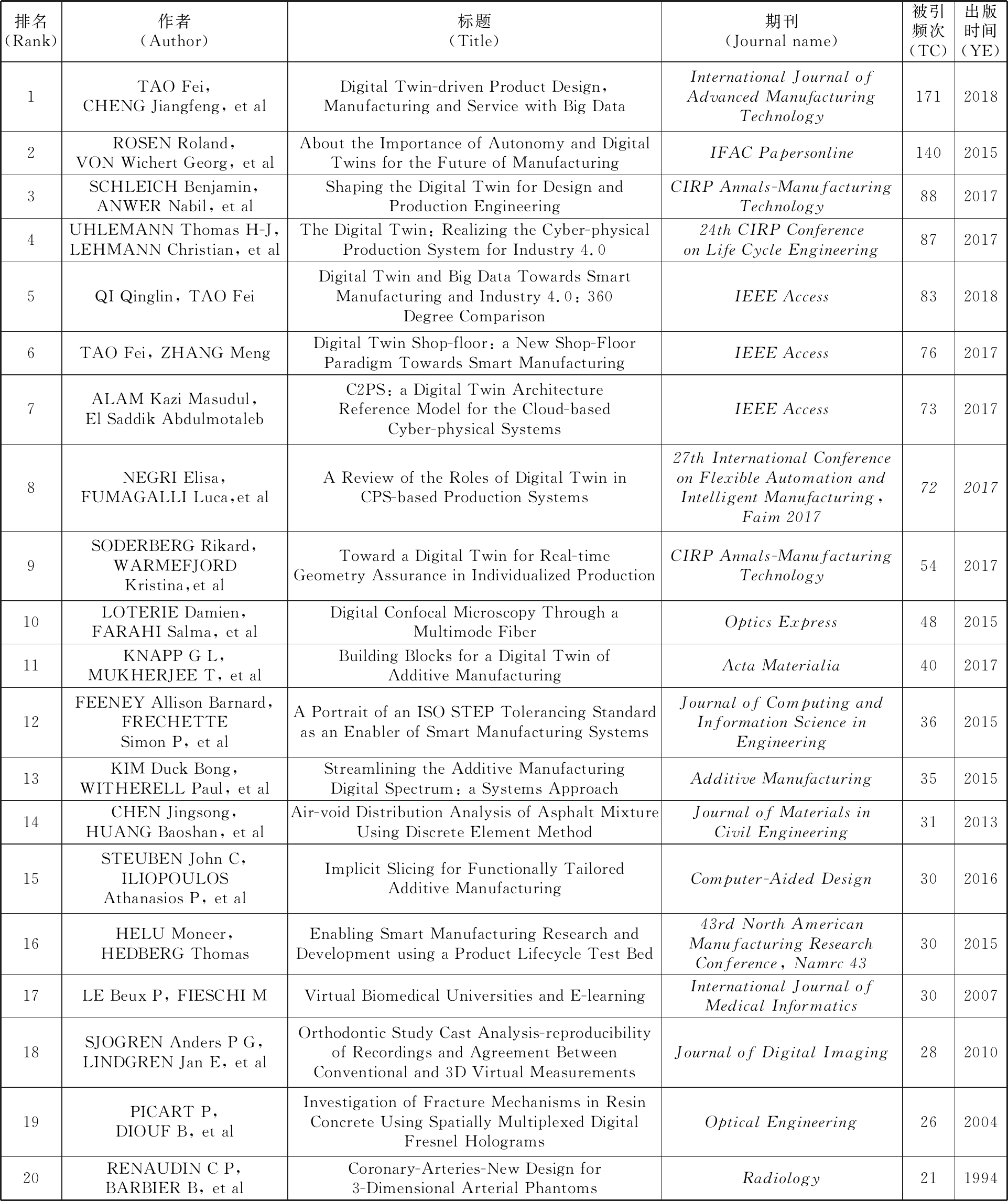
排名(Rank)作者(Author)标题(Title)期刊(Journal name)被引频次(TC)出版时间(YE)1TAO Fei,CHENG Jiangfeng, et alDigital Twin-driven Product Design, Manufacturing and Service with Big DataInternational Journal ofAdvanced ManufacturingTechnology17120182ROSEN Roland,VON Wichert Georg, et alAbout the Importance of Autonomy and DigitalTwins for the Future of ManufacturingIFAC Papersonline14020153SCHLEICH Benjamin,ANWER Nabil, et alShaping the Digital Twin for Design andProduction EngineeringCIRP Annals-ManufacturingTechnology8820174UHLEMANN Thomas H-J,LEHMANN Christian, et alThe Digital Twin: Realizing the Cyber-physicalProduction System for Industry 4.024th CIRP Conferenceon Life Cycle Engineering8720175QI Qinglin, TAO FeiDigital Twin and Big Data Towards SmartManufacturing and Industry 4.0: 360Degree ComparisonIEEE Access8320186TAO Fei, ZHANG MengDigital Twin Shop-floor: a New Shop-FloorParadigm Towards Smart ManufacturingIEEE Access7620177ALAM Kazi Masudul,El Saddik AbdulmotalebC2PS: a Digital Twin ArchitectureReference Model for the Cloud-basedCyber-physical SystemsIEEE Access7320178NEGRI Elisa,FUMAGALLI Luca,et alA Review of the Roles of Digital Twin inCPS-based Production Systems27th International Conferenceon Flexible Automation andIntelligent Manufacturing,Faim 20177220179SODERBERG Rikard,WARMEFJORDKristina,et alToward a Digital Twin for Real-timeGeometry Assurance in Individualized ProductionCIRP Annals-ManufacturingTechnology54201710LOTERIE Damien,FARAHI Salma, et alDigital Confocal Microscopy Through aMultimode FiberOptics Express48201511KNAPP G L,MUKHERJEE T, et alBuilding Blocks for a Digital Twin ofAdditive ManufacturingActa Materialia40201712FEENEY Allison Barnard,FRECHETTESimon P, et alA Portrait of an ISO STEP Tolerancing Standardas an Enabler of Smart Manufacturing SystemsJournal of Computing andInformation Science inEngineering36201513KIM Duck Bong,WITHERELL Paul, et alStreamlining the Additive ManufacturingDigital Spectrum: a Systems ApproachAdditive Manufacturing35201514CHEN Jingsong,HUANG Baoshan, et alAir-void Distribution Analysis of Asphalt MixtureUsing Discrete Element MethodJournal of Materials inCivil Engineering31201315STEUBEN John C,ILIOPOULOSAthanasios P, et alImplicit Slicing for Functionally TailoredAdditive ManufacturingComputer-Aided Design30201616HELU Moneer,HEDBERG ThomasEnabling Smart Manufacturing Research andDevelopment using a Product Lifecycle Test Bed43rd North AmericanManufacturing ResearchConference, Namrc 4330201517LE Beux P, FIESCHI MVirtual Biomedical Universities and E-learningInternational Journal ofMedical Informatics30200718SJOGREN Anders P G,LINDGREN Jan E, et alOrthodontic Study Cast Analysis-reproducibilityof Recordings and Agreement BetweenConventional and 3D Virtual MeasurementsJournal of Digital Imaging28201019PICART P,DIOUF B, et alInvestigation of Fracture Mechanisms in ResinConcrete Using Spatially Multiplexed DigitalFresnel HologramsOptical Engineering26200420RENAUDIN C P,BARBIER B, et alCoronary-Arteries-New Design for3-Dimensional Arterial PhantomsRadiology211994
注:统计数据截至2019-11-10。
2.8 数字孪生未来的研究方向
数字孪生自提出以来,在装备维护与智能制造方面展现出了良好的发展前景。近年来的研究热点主要围绕数据链、物联网以及虚拟现实等关键词展开。随着数字化技术的进一步发展以及传感技术的日益成熟,物理实体的精确全域感知技术、数字副本精准建模技术、基于人工智能和边缘计算等的数据快速分析处理与可视化呈现技术将是数字孪生未来重点研究与攻关的方向,基于虚拟制造、软件定义、数据驱动的未来智能工厂新型生产模式将在越来越多的工业企业中开展应用与实证研究。
3 结论
通过文献计量法分析,数字孪生相关论文数量在2015年开始迅速增加,并在2018年达到单年发表量的顶峰。美国、中国、德国、英国与法国发表数字孪生相关论文在所有国家/地区中排名前五,同时这些国家/地区积极参与到数字孪生的国际化研究当中,是对数字孪生研究贡献最大的国家/地区。目前数字孪生仍处于起步阶段,论文数量与论文被引数相对较少,但由于其具有可挖掘性强、应用领域广泛的特点,在未来将吸引更多的学者对其进行更为深入的研究。
来自以上国家/地区的ROSSMANN、TAO Fei与HEDBERG等已成为数字孪生领域研究的主要学者,他们在电气工程、计算机技术和工程制造领域展开了较为深入的数字孪生研究,并创造性地提出了数字孪生车间、数字孪生驱动和数字孪生生产线等概念,这与基于大数据的机器学习、物联网技术的广泛应用存在着密切的联系。发表数字孪生的期刊较为分散,但是伴随数字孪生技术的不断发展,将会有更多的期刊发表相关论文。
数字孪生技术作为解决物理世界与信息世界信息互联的一种重要方法,伴随中国对智能制造需求的不断提高以及信息技术的日益成熟,会被越来越多地应用到生产制造过程当中。
[1] CHWSHMEHDOOST A, STROUMBOULIS S , O’CONNOR B , et al. Dynamic Characteristics of a Resonating Force Transducer[J]. Sensors and Actuators A (Physical), 1994, 41(1/3):74-77.
[2] GRIEVES M. Digital Twin:Manufacturing Excellence through Virtual Factory Replication[EB/OL].[2016-12-20]. https:∥www.researchgate.net/publication/275211047_Digital_Twin_Manufacturing_Excellence_through_Virtual_Factory_Replication.
[3] GRIEVES M .Virtually Perfect: Driving Innovative and Lean Products through Productlifecycle Management[M]. Cocoa Beach: Space Coast Press,2011.
[4] SHAFTTOS M, CONROY M, DOYLE R, et al. NASA Technology Roadmap: Modeling Simulation Information Technology Processing Roadmap Technology Area[J/OL].[2017-10-09]. https:∥www.researchgate.net/publication/280310295_Modeling_Simulation_Information_Technology_and_Processing_Roadmap.
[5] TUEGEL E J, INGRAFFEA A R, EASON T G, et al. Reengineering Aircraft Structural Lifeprediction Using a Digital Twin[J].International Journal of Aerospace Engineering,2011,2011:1-14.
[6] KRAFT E M. The US Air Force Digital Threaddigital Twin-life Cycle Integration and Use of Computational and Experimental Knowledge[C]∥Proceeding of 54th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting. San Diego, 2016: 1-12.
[7] THOMAS H J,SCHOCK C,LEHMANN C, et al. The Digital Twin: Demonstrating the Potential of Real Time Data Acquisition Inproduction Systems[J].Procedia Manufacturing,2017,9:113-120.
[8] TUEGEL E J , INGRAFFEA A R , EASON T G , et al. Reengineering Aircraft Structural Life Prediction Using a Digital Twin[J]. International Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2011, 2011:1-15.
[9] TAO F, CHENG J F, QI Q L, et al. Digital Twin-driven Product Design, Manufacturing and Service with Big Data [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2018, 94(9/12): 3563-3576.
[10] SCHLEICH B , ANWER N, MATHIEU L,et al. Shaping the Digital Twin for Design and Production Engineering[J]. CIRP Annals - Manufacturing Technology,2017,66(1):141-144.
[11] NEGRI E , FUMAGALLI L , MACCHI M . A Review of the Roles of Digital Twin in CPS-based Production Systems[J]. Procedia Manufacturing, 2017, 11:939-948.
[12] ALAM K M, SADDIK A. C2PS: a Digital Twin Architecture Reference Model for the Cloud-based Cyber-physical Systems[J].IEEE Access,2017, 5:2050-2062.
[13] TAO F, ZHANG M. Digital Twin Shop-floor: a New Shop-floor Paradigm towards Smart Manufacturing [J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5:20418-20427.
[14] QI Q L, TAO F. Digital Twin and Big Data towards Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0: 360 Degree Comparison [J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6:3585-3593.
[15] ZHANG H, LIU Q, CHEN X, et al. A Digital Twin-based Approach for Designing and Multi-objective Optimization of Hollow Glass Production Line [J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5:26901-26911.
[16] LIU T, ZHANG L, YANG Y, et al. A Novel Cloud-based Framework for the Elderly Healthcare Services Using Digital Twin [J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7:49088-49101.
[17] FRAGA-LAMAS P, FERNANDEZ-CARAMES T M. A Review on Blockchain Technologies for an Advanced and Cyber-Resilient Automotive Industry [J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7:17578-17598.
[18] LAAKI H, MICHE Y, TAMMI K. Prototyping a Digital Twin for Real Time Remote Control over Mobile Networks: Application of Remote Surgery [J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7:20325-20336.
[19] XU Y, SUN Y M, LIU X L, et al. A Digital-twin-assisted Fault Diagnosis Using Deep Transfer Learning [J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7:19990-19999.
[20] LIU J F ,ZHOU H G,LIU X J, et al.Dynamic Evaluation Method of Machining Process Planning Based on Digital Twin[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7:19312-19323.
[21] ZHAO R L, YAN D X, LIU Q, et al. Digital Twin-driven Cyber-physical System for Autonomously Controlling of Micro Punching System [J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7:9459-9469.
[22] BONNARD R, HASCOET J Y, MOGNOL P, et al. STEP-NC Digital Thread for Additive Manufacturing: Data Model, Implementation and Validation [J]. International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 2018, 31(11): 1141-1160.
[23] DAMJANOVIC-BEHRENDT V, BEHRENDT W. An Open Source Approach to the Design and Implementation of Digital Twins for Smart Manufacturing [J]. International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 2019,32(3):1-19.
[24] HAN Y S, LEE J, LEE J, et al. 3D CAD Data Extraction and Conversion for Application of Augmented/Virtual Reality to the Construction of Ships and Offshore Structures[J].International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 2019,32(7):658-668.
[25] DELBRUGGER T, ROSSMANN J. Representing Adaptation Options in Experimentable Digital Twins of Production Systems [J]. International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 2019,32(4/5):352-365.
[26] PARK K T, NAM Y W, LEE H S, et al. Design and Implementation of a Digital Twin Application for a Connected Micro Smart Factory [J]. International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 2019,32(9):596-614.
[27] PARK K T, IM S J, KANG Y S, et al. Service-oriented Platform For Smart Operation of Dyeing and Finishing Industry [J]. International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 2019, 32(3): 307-326.
[28] NIKOLAKIS N, ALEXOPOULOS K, XANTHAKIS E, et al. The Digital Twin Implementation for Linking the Virtual Representation of Human-based Production Tasks to Their Physical Counterpart in the Factory-floor [J]. International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 2019, 32(1): 1-12.
[29] SLAVKOVIC N, ZIVANOVIC S, MILUTINOVIC D. An Indirect Method of Industrial Robot Programming for Machining Tasks Based on STEP-NC [J]. International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 2019, 32(1): 43-57.
[30] STURM L D, WILLIAMS C B, CAMELIO J A, et al. Cyber-physical Vulnerabilities in Additive Manufacturing Systems: a Case Study Attack on the STL File with Human Subjects [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2017, 44(1):154-164.
[31] ANGRISH A, STARLY B, LEE Y S, et al. A Flexible Data Schema and System Architecture for the Virtualization of Manufacturing Machines (VMM) [J].Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2017, 45:236-247.
[32] LU Y Q, XU X. Resource Virtualization: a Core Technology for Developing Cyber-physical Production Systems [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2018, 47:128-140.
[33] BONNARD R, HASCOET J Y, MOGNOL P, et al. Hierarchical Object-oriented Model(HOOM) for Additive Manufacturing Digital Thread [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2019, 50:36-52.
[34] CORONADO P D U, LYNN R, LOUHICHI W, et al. Part Data Integration in the Shop Floor Digital Twin: Mobile and Cloud Technologies to Enable a Manufacturing Execution System [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2018, 48:25-33.
[35] YAN X Y, BALLU A. Tolerance Analysis Using Skin Model Shapes and Linear Complementarity Conditions [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2018, 48:140-156.
[36] SODERBERG R, WARMEFJORD K, CARLSON J S, et al. Toward a Digital Twin for Real-time Geometry Assurance in Individualized Production[J].CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology,2017,66(1): 137-140.
[37] TAO F, ZHANG M, LIU Y S, et al. Digital Twin Driven Prognostics and Health Management for Complex Equipment [J]. CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology, 2018, 67(1): 169-172.
[38] MORSE E, DANTAN J Y, ANWER N, et al. Tolerancing: Managing Uncertainty from Conceptual Design to Final Product [J]. CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology, 2018, 67(2): 695-717.
[39] SODERBERG R, WARMEFJORD K, MADRID J, et al. An Information and Simulation Framework for Increased Quality in Welded Components [J]. CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology, 2018, 67(1): 165-168.
[40] HELU M, JOSEPH A, HEDBERG T. A Standards-based Approach for Linking As-planned to As-fabricated Product Data [J]. CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology, 2018, 67(1): 487-490.
[41] ZHUANG C B, LIU J H, XIONG H. Digital Twin-based Smart Production Management and Control Framework for the Complex Product Assembly Shop-floor [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2018, 96(1/4): 1149-1163.
[42] CHENG Y, ZHANG Y P, JI P, et al. Cyber-physical Integration for Moving Digital Factories Forward towards Smart Manufacturing: a Survey [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2018, 97(1/4): 1209-1221.
[43] LIU J F, ZHOU H G, TIAN G Z, et al. Digital Twin-based Process Reuse And Evaluation Approach for Smart Process Planning [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2019, 100(5/8): 1619-1634.
[44] TOQUICA J S, ZIVANOVIC S, ALVARES A J, et al. A STEP-NC Compliant Robotic Machining Platform for Advanced Manufacturing [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2018, 95(9/12): 3839-3854.
[45] GUO F Y, ZOU F, LIU J H, et al. Working Mode in Aircraft Manufacturing Based on Digital Coordination Model [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2018, 98(5/8): 1547-1571.
[46] SCHROEDER G N, STEINMETZ C, PEREIRA C E, et al. Digital Twin Data Modeling with Automation ML and a Communication Methodology for Data Exchange [J]. IFAC Papersonline, 2016, 49(30): 12-17.
[47] ROSEN R, von WICHERT G, LO G, et al. Aboutthe Importance of Autonomy and Digital Twins for the Future of Manufacturing [J]. IFAC Papersonline, 2015, 48(3): 567-572.
[48] WEYER S, MEYER T, OHMER M, et al. Future Modeling and Simulation of CPS-based Factories: an Example from the Automotive Industry [J]. IFAC Papersonline, 2016, 49(31): 97-102.
[49] SCHLUSE M, ATORF L, ROSSMANN J, et al. Experimentable Digital Twins for Model-based Systems Engineering and Simulation-based Development [C]∥2017 11th Annual IEEE International Systems Conference. New York,2017: 628-635.
[50] SCHLUSE M, ROSSMANN J. From Simulation to Experimentable Digital Twins Simulation-based Development and Operation of Complex Technical Systems [M]. New York: IEEE, 2016.
[51] ZHANG M, ZUO Y, TAO F, et al. Equipment Energy Consumption Management in Digital Twin Shop-floor: a Framework and Potential Applications [C]∥2018 IEEE 15th International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control. Zhuhai, 2018: 17769520.
[52] TAO F, ZHAN H, LIU A, et al. Digital Twin in Industry: State-of-the-art [J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2019, 15(4): 2405-2415.
[53] HELU M, HEDBERG T. Enabling Smart Manufacturing Research and Development Using a Product Lifecycle Test Bed [C]∥43rd North American Manufacturing Research Conference.Amsterdam,2015: 86-97.
[54] HEDBERG T, LUBELL J, FISCHER L, et al. Testing the Digital Thread in Support of Model-based Manufacturing and Inspection [J]. Journal of Computing and Information Science in Engineering, 2016, 16(2): 021001.
[55] SCHLUSE M, PRIGGEMEYER M, ATORF L, et al. Experimentable Digital Twins-streamlining Simulation-based Systems Engineering for Industry 4.0 [J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 14(4): 1722-1731.
